Cause allergy and treatment. Types and types of allergic reactions, diseases against the background of hypersensitivity of the body
Doctors distinguish several types and types of allergic reactions. The strength of the negative impact, the severity of symptoms and signs depends on many factors. With a decrease in immunity, high sensitivity of the body, health problems, a pronounced negative reaction is possible.
What types of allergies develop most often? What type of immune response does life threaten? Answers in the article.
An allergy to sesame seeds requires a restrictive diet. As with other food allergies, in this case, symptoms may include abdominal pain, but allergic or allergic acne can also occur. Sesame can also be the cause of the disease in the so-called cross allergy - then elimination often includes foods such as flour derived from cereals, nuts and kiwi.
Desensitization in the case of food allergies is usually not available, so in the case of this allergy, the only option is drugs that affect the symptoms of the disease. An allergy to sesame seeds does not mean, of course, that you should completely give up all sweets. However, be careful and buy these products at trusted allergy stores. You can also make sweets yourself, with proven foods that don't even contain trace amounts of sesame.
The mechanism of development of an allergic reaction

The negative response of the body proceeds according to a certain pattern:
- contact with an irritant;
- active production of antibodies, interaction with an allergen;
- the accumulation of certain substances, visible signs are absent;
- secondary contact with the allergen, binding of a foreign protein to antibodies, active reaction;
- with a fulminant type of allergy, all tissues and some organs are involved in the process, clinical signs of the disease quickly arise;
- with a delayed type of allergy, certain cells are sensitive to the stimulus. With the accumulation of a hazardous substance, active destruction of cells occurs in which the concentration of allergen is too high for normal functioning;
- excessive production of immunoglobulin E is a serious violation of the immune system. All types of allergies adversely affect the health of the patient.
Causes and triggers
A negative response with skin symptoms, the appearance of respiratory symptoms, and a worsening of the general condition develops when immune cells interact with various kinds of irritants. The strength of the reaction - from mild to dangerous, life-threatening. The more histamine in the short period enters the bloodstream, the brighter the negative response.
Sesame can also be found in other products. It should be remembered that in the case of people with hypersensitivity, also be careful with sesame oil, which is sometimes added to cosmetics. Although in this case the allergen will not act directly on the digestive system, it can cause allergy symptoms in the place where cosmetics with sesame oil will be applied.
A fur allergy affects a fairly large group of people. This allergen usually enters the body through the airways and causes symptoms similar to those in the case of pollen allergies. These include hay fever and watery eyes. However, you do not always have to throw an animal - desensitization is possible with this allergy.
The main allergens:
- medicines;
- some products;
- pollen;
- cold;
- animal hair;
- household chemicals;
- house dust;
- mold;
- varnishes, paints, pesticides;
- sunlight;
- wool and saliva of animals.
Provoking factors:
Important! The individual sensitivity of the body is a characteristic sign of allergy: for one person, citrus fruits are a powerful irritant, and the other, without prejudice to health, consumes juicy fruits. The same situation with antibiotics, plant pollen, animal hair.
A fur allergy is the most common allergy to a cat. Contrary to appearance, the problem should not only be the fur, but also the epidermis of the cat. Sensitive cats - black and very soft hair. Often these are short-haired breeds that cause allergies - in the case of long hair, thick, sensitization occurs less frequently.
Cat allergies are less common when the animal is completely white. Therefore, such animals are more often recommended for allergy sufferers. Also often talk about the possibility of acquiring a purebred cat, which generally does not have fur. However, due to the fact that sensitization causes cat skin, it is necessary to wash the cat. If the cat is already at home, you can try to reduce the amount of allergen in the air by wiping the animal’s coat with a damp cloth.
Types and stages
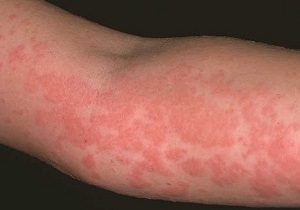
Classification by area of \u200b\u200bexposure to the stimulus:
- skin reactions ();
- respiratory reactions (effects on the nasopharynx and respiratory tract);
- common signs (violation of the cardiovascular, digestive system, central nervous system);
- enteropathy;
- damage to the eye area.
Classification of allergic reactions by type of irritant:
Strawberry allergies, as well as allergies to citrus fruits, are very common sensitization. What you should know about this type of allergy and what to do if you experience symptoms after eating these fruits? It should be remembered that a fruit allergy can be caused by a number of factors. In the case of strawberries, red pigment and salicylates are considered as a sensitizer. In case of symptoms such as urticaria, irritation of the mucous membranes of the oral cavity or the appearance of a red itchy rash after taking fruit, it is worthwhile to perform allergy tests.
Sometimes the symptoms of the gastrointestinal tract that appear after eating strawberries do not have to be caused by the fruit itself. It happens that the cause of allergies is spraying or germs. It should be remembered that in the case of people who are allergic to strawberries, the symptoms can be caused not only by fresh fruits, but also products that have strawberries.
- Humoral. Reasons: taking antibiotics, analgesics, sulfonamides, B vitamins, radiopaque substances, NSAIDs. Signs: impaired heart function, decreased immunity, general weakness, anemia.
- Anaphylactic. A dangerous type of immune response. Damage to the central nervous system is observed, all skin integuments are involved in the process, some mucous membranes (in the mouth, nasopharynx) are irritated. An acute reaction occurs in the first hours after contact with an allergen, lasts about a week. Often required hospitalization, comprehensive treatment to restore all body functions.
- Immunocomplex. Symptoms affect many organs and systems. The main factor is the intake of certain types of drugs.
- Local reactions. Negative signs occur on the face and body in contact with an allergen. Rashes, itching, swelling or pronounced swelling, burning appear on the background of the body's hypersensitivity to a certain substance.
Stages of allergic reactions:
In case of severe respiratory symptoms, it is necessary to abandon the use of strawberries and the use of drugs prescribed by an allergist. It should be remembered that this allergy can occur in both children and adults, but its gradual disappearance usually occurs only in the first case. Due to the fact that strawberries are a fairly strong allergen, it is not recommended to eat their breast-feeding women. If it is impossible to eat regular strawberries, you can try replacing them with a special type of white strawberry.
What are the symptoms of an allergy? How to recognize an allergy so as not to confuse it with a viral or bacterial infection of the upper respiratory tract? And finally, which allergy medications are effective? Allergies are an inappropriate response of the immune system to specific factors called allergens. Sensitizing allergens include many substances found in the human environment, this.
- first stage. It starts from the period of contact with the allergen until the first visible signs appear;
- second phase. The pathophysiological stage is accompanied by impaired functioning of organs and systems;
- third stage. The clinical stage is a period of time, which is characterized by the rapid development of negative symptoms.
Allergic diseases
To prevent dangerous symptoms, it is important to know why various types of reactions occur. The characteristic of the main diseases with hypersensitivity of the body is useful information for people of different ages. Subject to preventive measures, there is a real chance to avoid the development of acute and chronic allergies.
Pollen, dust mites, food, chemicals. . During the first contact with an allergen, the body often does not show signs of allergy. An allergic reaction can occur only at the next contact with a sensitive substance. Allergies are usually chronic and require systematic treatment.
Food allergies most often occur after ingestion. Cow's milk, nuts, tomatoes, chocolate, chicken egg white, citrus fruits, beef, veal. The first symptoms of food allergies include bloating, intestinal colic, loss of appetite, bad mouth odor, and anal itching. The treatment of food allergies is primarily the elimination of foods that cause an allergic reaction. If the so-called elimination of the diet does not help, consult your doctor who will carry out the appropriate pharmacological treatment.

In treatment, an integrated approach is important:
- elimination of contact with an allergen or minimization of negative effects on the body;
- it is mandatory to take antihistamines in the form of tablets. Children are prescribed syrups and drops;
- prevents a new rash and swelling hypoallergenic diet;
- a good antipruritic, decongestant effect is given by herbal baths and lotions, medicinal teas;
- gels, ointments and creams for allergies are prescribed to relieve itching, redness;
- recommended reception. The components of the funds quickly bind and remove toxins, allergens from the body, cleanse the intestines;
- with active peeling of the skin, cracks, hyperemia, emollients are prescribed for nutrition, moisturizing, eliminating burning, itching;
- apply only in severe allergies, short course.
Hives
Features:
Food allergies are characterized by the appearance. Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, constipation, abdominal pain. . Food allergies very often affect young children because their digestive system is still immature. In infants, the main allergen is milk and eggs. Older children have peanuts and fish.
Symptoms of food allergies in children are usually eczema on the face, as well as loose stools, colic and vomiting. If you suspect that your child or grandson may have an allergy, do not wait - contact your pediatrician. Depending on how the allergen enters the human body, there are four main types of allergies. Allergic reactions can be caused by allergens.
- signs occur in children and adults;
- blisters (pale pink or crimson) or red spots are noticeable on the body;
- the symptoms are similar to traces after a nettle burn;
- negative signs develop suddenly, itching worries, after taking pills for allergies, exclusions of contact with the rash irritant disappear without a trace;
- It causes many factors: food, cold, strong wind, UV rays, friction of clothing parts, taking medications.
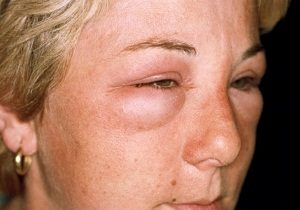
Quincke's edema
Inhaled, touched, swallowed, introduced into the body. . Thus, we distinguish between inhalation, contact, food allergology and poisonous allergies. The most common allergies include. Allergy to a cat or dog, or rather, to the hair of these pets.
The most common allergy symptoms are: hay fever, perennial rhinitis, asthma, and food allergies with skin rashes, vomiting, diarrhea, hives, or itching. It is very important not to confuse the symptoms of allergies with the symptoms of a viral or bacterial infection of the respiratory tract. This is the first and necessary step for proper treatment. The characteristics of allergies are a large amount of water secretion from the nose, the absence of elevated body temperature and the absence of typical pain in muscles and joints.
Characteristic:
- - acute allergic reaction of lightning type;
- main reasons: taking antibiotics, sulfonamides, analgesics, some products. Angioneurotic edema often occurs after a bee or wasp sting, especially in the area of \u200b\u200bthe face, tongue, eyes;
- pronounced swelling of the face, lips, cheeks, eyelids, crimson blisters are visible on the body, diameter - 5 mm to 10 cm or more. Tissues swell at high speed, blisters brighten, red border surrounds the edges;
- the tongue swells noticeably, the palate, the larynx, the patient suffocates;
- edema appears on the internal organs. Signs of dangerous reactions: headache, stomach ache, discomfort is felt in the chest area, genitals;
- to save life, the patient must take a fast-acting antihistamine, for example, or. Mandatory call "ambulance", especially with the development of angioedema in children. An acute reaction must be quickly stopped (there is no more than half an hour in stock), otherwise a fatal outcome is possible with suffocation on the background of compression of the larynx.
Atopic dermatitis
Signs:
If you have a cold every year at the same time and complain of sore throat and sinuses, and at the same time you do not have a fever - you are probably suffering from allergies. Allergy symptoms often depend on how the allergen got into our body. If you are allergic to pollen, the most common symptoms are hay fever, cough, and blocked sinuses. If we have a food allergy, we recognize it after hives and digestive problems.
Contact allergy or skin sensation is manifested by sensitization. Usually this is a rash that occurs exactly where the skin was in contact with this allergen. In such cases, allergy tests are useful for identifying allergens. Unfortunately, an allergy is a disease for which it is difficult to find an effective remedy. The patient must first avoid the allergen or, if possible, completely exclude him from his environment. If avoiding allergens does not help, you should go for treatment.
- an allergic disease develops in babies up to a year, subject to the rules of treatment and prevention, atopy gradually wanes, by the age of five the negative symptoms disappear;
- sometimes hypersensitivity to irritants lasts a lifetime, manifests itself in adults;
- crusts, redness, rashes are noticeable on the body, severe itching is disturbing. Localization of manifestations: knees, cheeks, forehead, chin, elbows, skin folds;
- negative symptoms intensify after eating foods with a high risk of allergies, against a background of weakened immunity, chronic diseases, problems with the digestive tract.
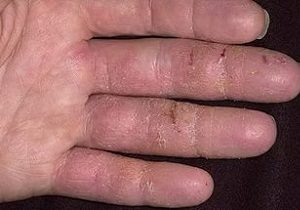
Eczema
Allergy treatment is usually symptomatic. In pharmacies, we find many allergy medications, also available over-the-counter. Allergy pills are mainly antihistamines that prevent symptoms such as. Swelling of the mucous membranes, itching, hives. . Another type of allergy is glucocorticoids, which have a strong anti-inflammatory effect. Both types of medications can be used orally, intravenously, inhaled, nasally and on the skin.
Allergy eye drops and nasal sprays called cronones are also helpful. Allergies also apply to medicines that contract blood vessels. Sometimes doctors recommend specific immunotherapy, which includes repeated administration of an increasing number of doses of an allergenic vaccine, to which the patient is allergic. Thanks to immunotherapy, the patient's body becomes less sensitive to the allergen.
Characteristic:
- severe chronic disease of a neuro-allergic nature;
- the patient is concerned about skin reactions: peeling of the epidermis, itching, redness, crusts, weeping. Papules appear, after opening, serous wells form, often secondary infection develops;
- frequent stresses, weak immunity, chronic pathologies, enhance symptoms;
- during the lull period, acute symptoms are almost invisible, the epidermis thickens, a specific skin pattern appears, the skin is slightly peeling;
- treatment is long and not always successful;
- the result of therapy largely depends on the patient: only exact adherence to the rules pushes the next attack for several years, otherwise, exacerbations occur every 4-5 weeks.
Food allergy
Features:
Allergy patients should also use a vacuum cleaner calendar, which monthly contains information on the concentration of allergens in the air. Allergy patients should plan a vacation trip with this calendar. In summer, special attention should be paid to healthy tanning. It may turn out that we are allergic to the sun. This is why it is always helpful to buy lime for allergies before you go.
Below we provide a brief description of the individual subjects of the disease. Allergic inflammation of the nasal mucosa. Allergic rhinitis is caused by inhaled pollen antigens that occur during pollination of trees, shrubs, grasses and weeds. The disease is characterized by attacks of sneezing, an itchy nose, an increased amount of watery secretion in the nose and a sensation of its so-called clogging. a nasal blockage that prevents breathing. Some people may also have impaired sense of smell and headaches.
- the reason is the use of certain foods;
- if a particular type of food is an irritant for a person, then the reaction can be severe, up to development;
- the immune system is involved in the process, with skin symptoms develops with lesions of the digestive tract;
- main signs: red dots or spots on the body, swelling of tissues, hyperemia, itching, nausea, abdominal pain, lowering pressure;
- during treatment and after recovery, products provoking allergic reactions are excluded from the menu.
How and what to treat? Learn effective and safe methods.
Quite often, secondary inflammation of the sinuses, sleep disorders and the patient's ability to concentrate develop. Quite often, nasal symptoms are accompanied by conjunctival symptoms such as tearing, redness, photophobia, and itching, or from the throat, such as a cough.
In patients, the most common are sensitization to grass and cereal pollen, pollen and fly agaric. Allergic rhinitis occurs in the form of chronic perennial rhinitis with symptoms persisting throughout the year, or seasonal hay fever, most often occurring during the pollination of trees and grasses. The time of onset of symptoms is closely related to the date of flowering of the plants with which the patient is sensitized.
Effective methods of treating cold allergies in the hands are described on the page.
Go to the address and read about how to properly take egg shells from allergies in children and adults.
Contact dermatitis
Features:
- the reason is the effect of the stimulus on certain parts of the body. Often negative symptoms appear on the hands, forearms;
- allergens: household chemicals, oils, acids, solvents, varnishes, disinfectants. Poor cosmetic products, washing powders, hair dyes are dangerous;
- the area of \u200b\u200blocalization of negative symptoms allows you to quickly determine why blisters, small rash, redness, appeared;
- after recovery, refusal from irritating compounds, protection of the skin of the hands when working with chemicals is mandatory.
Bronchitis

Features:
- penetration of aeroallergens provokes without sputum, wheezing, sore throat. Nasal congestion appears, mucus is viscous, it is difficult to cough up;
- disturbed by sneezing, paroxysmal cough develops at night;
- often markedly increased sweating, weakness appears;
- a blood test shows an increase in the level of eosinophils;
- pills and cough syrups do not bring noticeable relief. Until the patient accepts, the symptoms will not disappear.
Rhinitis
Irritants:
- pollen of ragweed, alder, birch, milkweed, loboda, poplar fluff;
- mold;
- powders, aerosols for home care, laundry detergents;
- animal hair.
Often accompanies diseases with high sensitivity to irritants.
Key features:
- nasal congestion;
- liquid mucus constantly flows from the nasal passages. The discharge is odorless and colorless, the nature of the mucus does not change over time;
- ordinary drops in the nose do not help, special ones are needed;
- headache against the background of difficulty breathing, irritability, weakness;
- runny nose is often accompanied by allergic eye damage;
- characteristic signs cause discomfort seasonally (during the flowering period of some plants) or year-round (with allergies to pet hair, household dust, household chemicals).
Conjunctivitis
Features:

- one of the reactions with the seasonal and year-round type of negative response of the body, often develops simultaneously with a runny nose;
- signs: conjunctival redness, active, itching and swelling of the eyelids. The patient feels discomfort, sometimes photophobia develops. An unpleasant sign is peeling of the skin with an increase in the dryness of the epidermis on the eyelids;
- severe conjunctivitis leads to damage to the optic nerve, partial or complete loss of vision, pronounced corneal edema;
- causes: bacterial, viral and fungal infections, exposure to allergens, reaction to taking or instilling a certain medicine, eye surgery with suturing, wearing contact lenses;
- we need special, regular wet cleaning in the home, eye protection from pollen and fluff during seasonal reactions.
Knowing the signs, causes of the main types and types of allergies together with preventive measures preserves health. Strong immunity, elimination of contact with an irritant, absence of chronic pathologies, proper diet are factors that reduce the risk of relapse after stopping an allergic reaction.
Learn more about the types and types of allergic reactions in children after watching the following video:
Aallergy can manifest itself with a variety of symptoms from many organs and systems, and yet there are certain patterns and forms of allergies. Knowing the form of allergies, appropriate measures can be taken to alleviate the condition.
Respiratory allergyIs a form of an allergic reaction that occurs in response to the ingestion of allergens (aero allergens) from the air in the respiratory tract, such as house dust, plant pollen, animal hair particles, etc. The main forms of respiratory allergy are allergic rhinitis and atopic bronchial asthma.
Every twelfth resident of Russia suffers from bronchial asthma.
Allergic rhinitis (runny nose)- This is an inflammation of the nasal mucosa that occurs when airborne allergens enter. Its symptoms are generally the same as for rhinitis of an infectious nature caused by various pathogenic bacteria and viruses. They differ only in the cause that caused them and in the absence of the fever that is possible with infectious rhinitis. Allergic rhinitis is usually manifested by itching in the nose, sometimes throat and oral cavity, nasal congestion and profuse mucous discharge from it, repeated sneezing. These symptoms can occur within a few minutes after the patient contacts the allergen to which he is sensitive. Very often, signs of conjunctivitis join the symptoms of allergic rhinitis - itching and burning in the eyes, lacrimation, photophobia, swelling and redness of the eyelids. In this case, we are talking about allergic rhinoconjunctivitis.
The effect of drops from a runny nose weakens over time, and abuse of them leads to damage to the mucous membranes.
Allergic rhinitis can occur in three forms, such as seasonal allergic rhinitis, chronic and occupational allergic rhinitis.
Seasonal allergic rhinitis (hay fever, hay fever)- a type of respiratory allergy, which is characterized by a clear seasonality, limited strict calendar dates associated with the flowering period of plants whose pollen serves as an allergen for patients sensitive to it (for more details see below). In different climatic zones, the timing of flowering plants is different, therefore, the time of onset of symptoms of hay fever in patients from different regions is not the same.
During the flowering period of trees (May - early June), patients with hay fever need to exclude apples, plums, cherries, cherries, peaches, apricots from the diet. nuts, carrots, honey.
Hay fever is the most common form of allergy and in its scale resembles the SARS epidemic, however, it occurs only in the warm season. Signs of hay fever are no different from the general symptoms of allergic rhinitis (itching and burning in the nose, clear mucous discharge). They arise acutely, coincide with the beginning of flowering of the plant, to which the patient is sensitive, and usually completely disappear after flowering is completed. However, often one patient may experience an allergic reaction to pollen of several plants blooming at the same time or at certain intervals. Sometimes it happens that one patient is allergic to the pollen of plants blooming in spring, summer and autumn, for example, pollen from birch, dandelion and quinoa, and therefore almost the entire warm season is the most painful period for him.
At the beginning of the XX century. less than 1% of the world's population suffered from hay fever. Currently, this figure is already 10%, and the number of cases continues to increase.
Chronic (year-round) allergic rhinitisdue to contact with allergens that are in the air constantly, regardless of the time of year. These include house dust, pet hair, household cleaning products. Manifestations of chronic allergic rhinitis, as a rule, are less pronounced than hay fever, but have been observed almost constantly for many years. The patient is disturbed by a periodically arising feeling of nasal congestion, a meager or moderate discharge from it.
Occupational Allergic Rhinitisit is associated with a person’s contact at the workplace with dust of various origins or certain chemicals, to which he gradually becomes more sensitive. Manifestations of professional allergic rhinitis can be of varying degrees of intensity and occur only during work, i.e., when the patient contacts the allergen. On weekends and holidays, during the holidays, i.e. when the patient does not come in contact with the allergen, the manifestations of allergic rhinitis can completely disappear.
In some patients with long-term chronic allergic rhinitis, overgrowths of the nasal mucosa appear, which create an additional obstacle to normal breathing.
Bronchial asthma is a disease manifested by periodically occurring attacks of suffocation. There are several types of bronchial asthma, the development of which is associated with various causes. The so-called truly allergic nature atopic bronchial asthma, which usually develops already in childhood or adolescence in people with a hereditary predisposition to allergic diseases. It can occur in isolation, but more often develops against the background of other allergic diseases that the child already has.
The development of an attack of bronchial asthma has a complex mechanism. The sensitive mucous membrane of the bronchi of a person suffering from allergic diseases is too much responsive to the ingestion of allergen substances in the air on its surface. Upon contact with the allergen, the mucous membrane of the bronchi begins to secrete copious, thick mucus, which is distributed along the walls of the bronchi and narrows their lumen. The mucous membrane itself swells, thickens towards the lumen of the bronchi and narrows it even more. In addition, the muscular membrane of the bronchi reacts to the introduction of the allergen into the body, and there is a contraction of these muscles - bronchospasm. The lumen of the respiratory tract narrows significantly, and an attack of suffocation occurs. A feature of the asthma attack in bronchial asthma is that air is relatively easily supplied from the outside to the lungs by the muscles of the chest and abdomen, and comes back with difficulty. Therefore, the patient during an attack has shortness of breath on exhalation, he wheezes and coughs, trying to breathe out the accumulated air, his face turns red. After some time, the lumen of the bronchi expands, the air begins to go out with thick, viscous sputum, breathing is restored, and the attack ends. Such attacks adversely affect the well-being and general health of the patient. Bronchial asthma can be complicated by emphysema (lung tissue ruptures with a gradual deterioration of normal lung function), respiratory failure, or the transition of an attack to the so-called asthmatic status - a severe attack, which sometimes lasts up to several days and threatens the patient with death.
With an atopic form of bronchial asthma, asthma attacks can occur with every contact with an allergen. A very common is the everyday form of bronchial asthma, in which the allergen, i.e., the main cause of the asthma attack, is house dust, or rather, microscopic saprophytes that live in it. Pollen bronchial asthma associated with the pollen of one or more flowering plants, to which the patient is sensitive, is less common. Manifestations of this form of bronchial asthma are of a clear seasonal nature, whereas with household bronchial asthma, attacks can occur at any time all year round.
Over the past 15 years, the number of cases has doubled. Currently, about 300 million people worldwide suffer from asthma.
Allergic reactions from the respiratory organs can be associated not only with aeroallergens, but also with some bacteria. This is the so-called infectious allergy, or respiratory allergy. Some microbes that are not dangerous for most healthy people, getting into the respiratory tract of a person prone to allergic diseases, can form his hypersensitivity. And then, upon repeated contact with them, the patient shows signs of an allergic reaction from the respiratory system. An allergic reaction can occur with symptoms of allergic rhinitis or bronchial asthma.
Allergic conjunctivitis- This is a response of the mucous membrane of the eye (conjunctiva) to allergens in the form of the development of its inflammation.
Its main symptoms are generally the same as with conjunctivitis caused by other reasons. However, its development is due to the contact of the body with an allergen to which it is sensitive.
Common symptoms of conjunctivitis are itching or burning in the eyes, sometimes causing an irresistible desire to rub them, redness of the conjunctiva covering the inner surface of the eyelids and the entire visible surface of the eyeball, lacrimation, sometimes very pronounced, photophobia. The eyelids become reddened and swollen. These symptoms occur simultaneously in both eyes after some time (from several seconds to several hours) after the patient contacts the allergen. Typically, these manifestations are very pronounced and significantly disrupt the normal life of the patient, and sometimes so insignificant that the patient may not suspect for a long time that he has allergic conjunctivitis.
Allergic conjunctivitis is one of the most common forms of allergic reactions. Often, in one patient, allergic conjunctivitis is combined with one or more other allergic diseases - atopic dermatitis, allergic rhinitis, atopic bronchial asthma.
Despite the common symptoms, specialists distinguish several types of allergic conjunctivitis, each of which has its own characteristics of the course and treatment.
Sometimes the conjunctiva becomes so reddened that it seems that the patient has red eyes. Therefore, allergic conjunctivitis is also called "red eye disease."
There are hay fever conjunctivitis, spring keratoconjunctivitis, drug allergic conjunctivitis, chronic allergic conjunctivitis, allergic conjunctivitis when wearing contact lenses, professional allergic conjunctivitis and some other less common varieties.
Pollinous conjunctivitisarise only in the flowering season of plants whose pollen is an allergen to which the patient is sensitive. The exact time of occurrence of this disease depends on the climatic conditions in which the patient lives, and the associated flowering calendar of plants. The disease can occur in acute or chronic form. The acute form is characterized by rapid development with severe itching in the eyes, profuse lacrimation, photophobia and intense conjunctival edema. But more often this form of allergic conjunctivitis occurs chronically, i.e. with a mild burning sensation and itching and periodic exacerbations, which are characterized by symptoms of acute pollinosis conjunctivitis.
Spring keratoconjunctivitis (spring catarrh)usually begins in childhood and develops more often in boys. It proceeds chronically, is difficult to treat and causes considerable pain to the patient. In addition to the typical symptoms of allergic conjunctivitis, over time on the conjunctiva of the upper eyelid there are growths of the mucous membrane, small, flattened, or larger and convex. The lesion of the cornea of \u200b\u200bthe eye joins - its dense shell, completely covering the eyeball, and in its front part is covered with the conjunctiva. The cornea becomes inflamed, erosion or ulcers may appear.
Allergic conjunctivitismay occur as a reaction to the introduction of any drug, and not only in the eye. It can develop both with the first use of the drug, and (more often) with prolonged treatment of a chronic disease. An allergic reaction can develop at different times after the administration of the drug - from a few seconds to several days or weeks. The manifestations of drug allergic conjunctivitis can also be different in different people - from minor to very pronounced.
Chronic Allergic Conjunctivitisdevelops due to constant or frequent contact of the patient with allergens. As a rule, these are house dust, animal dander, food products, household chemicals and other substances with which a person comes into contact almost every day. Manifestations of this form of allergic conjunctivitis are usually mild or moderate. Over the years, the patient notes occasionally a slight burning sensation or itching in the eyes, scanty discharge, accumulating in the corners of the eyes in the morning. These symptoms sometimes appear, then disappear, and sometimes they are expressed so slightly that for a long time the patient does not pay attention to them.
According to doctors, allergic conjunctivitis when wearing contact lenses occurs in most people using them, after more or less time from the start of their use.
Allergic conjunctivitis when wearing contact lenses.An allergic reaction can occur both on substances that make up the lenses themselves and on lens care products. With the development of an allergic reaction, the patient begins to feel discomfort when wearing contact lenses, itching and burning in the eyes, lacrimation and photophobia appear. In some patients, small vesicles or growths in the form of papillae form on the conjunctiva.
Occupational Allergic Conjunctivitisdevelops when a person comes in contact with certain substances at his workplace, to which he eventually acquires increased sensitivity. The symptoms of professional allergic conjunctivitis in different people can be expressed to varying degrees, but they always remain the same throughout the entire working time all year round, and on non-working days, especially during the holiday period, they can completely disappear.
Allergic Dermatoses- These are skin lesions after exposure to an allergen. They can occur not only as a result of direct contact of the allergen with the skin surface of the patient, but also when allergens enter the body in other ways.
The main forms of allergic dermatitis are urticaria, allergic contact dermatitis and atopic dermatitis.
Hives- a common type of skin allergic reactions, which is manifested by the appearance on the patient’s skin of blisters similar to those that appear after touching stinging nettles. Urticaria occurs not only with direct contact of the patient's skin with the allergen, but also when it enters the body in other ways (through the organs of the digestive and respiratory systems).
Urticaria occurs acutely just a few minutes after contact with the allergen, when severe itching, burning, and then characteristic rashes - dense bright pink blisters protruding over the surface of normal skin, rounded form appear on any part of the skin, less often on the mucous membranes. Their size can range from a few mm to 10 - 15 cm. Blisters can merge with each other into larger formations.
After a few minutes or hours, the blisters pass without a trace (see chapter 8 Emergency conditions).
Allergic contact dermatitisoccurs only after direct contact with the skin of a sick allergen to which he is sensitive. Changes on the skin appear initially at the point of contact, but over time can spread to larger areas.
Sometimes large blisters, which occupy a vast area, can also affect the general well-being of the patient (body temperature rises, weakness, weakness appears), although usually the patients are not disturbed by urticaria.
Dermatitis begins acutely some time after exposure to an allergen. Initially, pronounced edema appears on this area of \u200b\u200bthe skin, the skin acquires a bright red color. Then, against this background, bubbles of various sizes appear, filled with liquid. After some time, the bubbles burst, and in their place shallow skin defects are formed - erosion, from the surface of which a clear or cloudy liquid constantly separates. Then the inflammation gradually disappears, the weeping disappears, and the erosion is covered with crusts or scales, and then heal completely, usually without leaving scars.
Atopic dermatitisdue to a hereditary predisposition to allergic diseases and manifests itself already in childhood. Characteristic changes in the skin with this disease can occur not only when it is in direct contact with the allergen, but also when the allergen enters the body in other ways. Atopic dermatitis can cause foods, pollen, animal hair, household chemicals.
The first symptoms of atopic dermatitis occur between birth and 2 years. On the skin of the face, trunk, limbs in the elbow and knee joints, itchy, flaking spots of bright red color appear. Such dermatitis may not respond to treatment for a long time.
After some time, atopic dermatitis usually disappears, but in some patients its symptoms may periodically appear throughout life. People who have had atopic dermatitis in childhood often suffer from neurodermatitis or eczema.
Allergic enteropathy- This is a lesion of the gastrointestinal tract in contact with an allergen. Moreover, allergic enteropathy can be caused not only by allergens that enter the digestive system directly through the mouth (food, drugs), but also in other ways, for example, through the organs of the respiratory system.
Allergic enteropathy can manifest itself as signs of damage to various parts of the digestive tract - from the oral cavity to the intestines, but more often they combine, and a whole complex of symptoms of allergic damage to the digestive system occurs, which, however, differ little from those with lesions of a different nature (for example, inflammatory).
So, some time after the patient’s contact with the allergen, nausea, vomiting, cramping pain localizing in different parts of the abdomen appear. Patients have stool disorders, often in the form of diarrhea. These symptoms may be accompanied by signs of allergic changes and other organs, such as the respiratory system (rhinitis), skin (urticaria). As contact with the allergen stops, the symptoms of allergic enteropathy gradually disappear.
Anaphylactic shock- This is the most severe form of allergy, in which the risk of death of the patient is very high. Frequent lethal outcomes during anaphylactic shock are associated with its sudden development and rapid, literally fulminant course. This form of allergy has no characteristic manifestations and is usually a collection of rapidly progressing symptoms characteristic of other forms of allergy.
Often anaphylactic shock begins a few minutes after the ingestion of an allergen or even at the time of its administration (for example, during an injection of a drug).
It is noted that the less time passes from the moment an allergen enters the body to the development of shock symptoms, the harder it is and the higher the risk of death.
The fight against anaphylactic shock should begin immediately when the first signs of anaphylaxis appear.
Often, even before the first visible signs of anaphylactic shock appear, patients may feel some anxiety, anxiety, or even a seemingly causeless (so far) fear of death. A feeling of hot flush may occur, skin sensitivity changes in the form of a tingling sensation, crawling or itching. Then the patient feels insurmountable weakness, complete impossibility to make any movement or speak, dizziness, headache, noise or a feeling of stuffiness in the ears appear, visual acuity may suddenly decrease. Symptoms characteristic of the defeat of a particular organ or system of organs: respiration, digestion, cardiovascular and nervous systems quickly join. Lesions of individual organ systems can be combined with each other and gradually progress. The defeat of the respiratory system manifests itself in the development of a respiratory tract spasm in the patient, while the breathing becomes shallow, rapid, may be accompanied by wheezing or the separation of foamy sputum. The patient makes considerable physical efforts to breathe, but as the shock progresses, asphyxia develops (state of suffocation). Violation of the function of the cardiovascular system is manifested by malfunctions of the heart muscle with an increase in heart rate, a weak pulse and a drop in blood pressure. Gastrointestinal upsets - nausea, vomiting, cramping pains throughout the abdomen, diarrhea with an admixture of blood. Damage to the nervous system - by convulsive contractions of individual muscle groups or convulsive seizures of the epileptic type.
With anaphylactic shock, the skin of the patient's face and body initially turns red, but then turns pale, fingers and hands can even acquire a bluish tint; the skin is covered with cold, sticky sweat. At first, motor anxiety is noticeable, the patient does not find a place for himself, makes random movements. Then cramps occur, urinary and fecal incontinence, the patient loses consciousness and falls into a coma. In this state, it is motionless, does not respond to external stimuli (sound, light, touch). Body temperature decreases, blood in the vessels thickens. Death with anaphylactic shock is associated with the onset of asphyxia or vascular insufficiency.
Sometimes the development of anaphylactic shock is preceded by the usual, it would seem, urticaria, allergic rhinitis, or any other type of allergy.
Types of allergic reactions
Household dust allergy- a fairly common phenomenon. In any house, even if the owners carry out regular wet cleaning, there will certainly be at least some amount of house dust. Its quantity may vary depending on the season, climatic conditions, as well as the type of room. In house dust, you can find particles of earth and sand that got into the house from the street, pet hair and many tiny particles of various objects in the house, as well as hair and dead scales of human skin. It is these scales that are the food for microscopic mites that live in house dust.
The amount of dust in the house is distributed unevenly - depending on the location of the house, climate, season. For example, in a village house there is less dust than in a city apartment, and even within the same house there is a difference between its amount in the bathroom and bedroom ....
These are very small arthropods, several tenths of a millimeter in size, resembling spiders in appearance. They are normal inhabitants of human housing and do not harm its owners, unless they are predisposed to allergic diseases. In people with allergies, the reaction does not occur to dust or ticks, but to their excrement. The greatest number of ticks can be found on carpets and carpets, as well as on human underwear and bedding. Most of all ticks like to live in a person’s bed, since the increased temperature and humidity created by the human body during sleep are optimally suited for the life of ticks.
Since house dust mites are in constant contact with a person, allergy phenomena disturb the patient all year round, but in autumn and winter they are more pronounced. Allergies to house dust mites usually occur in the form of typical allergic rhinitis or bronchial asthma, less commonly in the form of conjunctivitis. The attack begins when a person wakes up, because physical activity contributes to the "raising" of dust and getting it on the mucous membranes of the respiratory system and eyes.
House dust mites do not live in a dry mountain climate, so the area at an altitude of 1500 - 1800 m above sea level is favorable for people with allergies to house dust.
Animal allergy- also quite common.
The cause of allergic reactions in people prone to this can be both domestic and farm animals.
The source of allergies can be their various "parts" and waste products: wool, feathers, dandruff, saliva, urine and excrement. Allergies to animals begin immediately after contact with animals or objects that contain allergenic substances of animal origin. More often, an allergy to animals occurs in the form of allergic rhinitis, conjunctivitis or rhinoconjunctivitis. Atopic asthma and, rarely, urticaria are less common.
When the cats lick their hair, the clouds scatter whole clouds from the smallest droplets of saliva in the air - they are literally “sprayers” of allergies!
Almost immediately after contact with an animal or animal allergens, the patient begins to feel itching and burning in the eyes or nasal cavity, throat, lacrimation, nasal discharge, i.e., all typical signs of one or another form of allergic reaction. After termination of contact with the allergen, the symptoms quickly disappear. In the absence of contact with animal allergens, the patient may feel completely healthy if he has no other allergic or other diseases.
If one of the family members has a predisposition to allergic diseases, then you can not get an animal in any case.
Allergy to insect bites.Insect bites can have different effects on the human body. Bites of small blood-sucking insects (mosquitoes, midges, mosquitoes) usually do not cause an allergic reaction in a person, since these insects, when they bite, inject substances into the wound that slow down the normal coagulation of the person's blood in order to have enough time before the blood begins to clot. These anticoagulants cause people only burning and itching, which soon pass.
It happens quite differently when stinging with the so-called hymenopteran insects - bees, wasps, bumblebees, etc. In this case, poison is released into the wound, which, among other substances, includes a foreign protein. It is he who is an allergen for people prone to allergic diseases. Even in healthy people who do not suffer from allergic diseases, stinging hymenopteran insects causes extremely unpleasant sensations. The stinging site turns red, swollen and severely sore. The ingestion of a large amount of poison (for example, when bitten by several insects at once) causes, in addition to the described local signs, general symptoms of poisoning. A headache may occur, sometimes an increase in body temperature with chills, nausea, vomiting, even cramps occur. However, after a few hours or days, these symptoms disappear, and the person again feels healthy.
The same symptoms can occur in a person prone to allergic diseases, but only with the first sting. Then he develops an increased sensitivity to the poison of these insects, and repeated stings, if they occur, are accompanied by the development of signs of an allergic reaction, and with each new contact with the poison these reactions become more intense.
Sometimes at the first contact with bee venom in a person with increased sensitivity to it, in addition to edema and redness at the wound site, skin rashes appear. But more often, a local reaction is accompanied by general allergic manifestations. After stinging, urticaria or a respiratory allergic reaction with an attack of suffocation quickly develops. A large amount of poison in the body or repeated stings can cause anaphylactic shock with all its characteristic signs and possible consequences.
Food allergyoccurs in response to ingestion of allergen substances into the digestive system. They can be food products or medicines in the form of tablets, capsules, suspensions and other dosage forms taken orally (by mouth). A food allergy can affect any part of the digestive system with which the allergen comes in contact, from the oral cavity to the intestines, manifesting itself with certain symptoms.
Allergic damage to the oral cavity can be expressed by itching, swelling of the tongue, lips or a more extensive complex of symptoms - the so-called Quincke's edema (see chapter 8 Emergency conditions).
With damage to the esophagus, the patient may notice difficulty swallowing, worsening the passage of solid food, pain behind the sternum. Signs of stomach damage: pain, nausea, and vomiting. Allergic damage to the intestine is manifested by sharp cramping pains in various parts of the abdomen without a certain localization, diarrhea. Gastrointestinal bleeding can sometimes occur.
Severe allergic reactions can affect the liver. Its structure and functions are violated, the patient develops jaundice, the liver enlarges and becomes painful.
With the exclusion of certain foods from the diet, as well as refusal to take medications that cause allergies, the patient feels healthy and the symptoms described do not bother him.
Diseases associated with the delayed hypersensitivity reaction
Allergic diseases associated with the delayed-type hypersensitivity reaction are characterized by the delayed onset of allergy symptoms after exposure to the allergen. Hypersensitivity of the body is formed for a long time, so for a fairly long time, a particular substance may not cause any allergic manifestations in the patient, but up to a certain point. A rather striking example of allergic reactions of the type of delayed-type hypersensitization is drug allergyprimarily for antibiotics. This is especially noticeable on antibiotics used orally or as applications on the oral mucosa in some dental diseases. Long-term antibiotic treatment, carried out in this way, after a certain time, can cause local reactions in the form of toxic-allergic stomatitis in people predisposed to allergies. They come in several types.
According to the area of \u200b\u200bdamage to the oral mucosa, they are divided into fixed and common, and depending on the changes, they are catarrhal, catarrhal-hemorrhagic, erosive-ulcerative, ulcerative-necrotic.
Catarrhal toxic-allergic stomatitis is the most mild form of the disease. The general well-being of patients remains normal. Itching and burning of the oral mucosa occurs, it becomes reddened and swollen. On examination, fingerprints on the lateral surfaces of the tongue and cheeks are noticeable. Patients complain of a feeling of dry mouth and soreness when eating, associated with irritation of the sensitive inflamed mucous membrane in contact with pieces of food.
The catarrhal hemorrhagic form of the disease is characterized, in addition to the above symptoms, by the appearance of small hemorrhages on the oral mucosa, and sharp pieces of food injure the mucous membrane and cause minor bleeding. General well-being also does not change.
Erosive-ulcerative stomatitis is characterized by more pronounced changes. The mucous membrane of the cheeks, palate, gums, lips becomes red, swollen, and in some places bubbles form on it, filled with a clear liquid. They quickly burst, exposing shallow defects of the mucous membrane (erosion), covered with a whitish coating. Erosions can merge and form vast areas of damage. The sensation of dryness in the oral cavity intensifies, saliva is produced little, the mucous membrane is easily injured by pieces of food, bleeding occurs. The general condition of the patient may be disturbed. Possible increase in temperature to 37.5 - 38 ° C, malaise, an increase in nearby lymph nodes.
Ulcerative necrotic stomatitis is an even more severe form of the disease. This form rarely develops in isolation, much more often - as one of the manifestations of common severe allergic reactions affecting the whole body. Stomatitis is accompanied by impaired general condition. Body temperature is elevated, often to high numbers, appetite is reduced or completely absent, weakness, lethargy, and headaches are noted. The mucous membrane of the oral cavity is affected almost entirely. It is swollen, reddened, with extensive areas of yellowing-gray tissue death. Sections of the living mucosa are covered with a gray coating under which bleeding mucosal defects are exposed during removal. Such patients are concerned about pain in the mouth, especially when eating and talking, the characteristic sugary sweet smell from the mouth, salivation. The nearby lymph nodes are enlarged and painful on palpation.
With common toxic-allergic stomatitis, the symptoms also depend on the type of allergen. For example, with an allergy to penicillin, the tongue becomes bright red, its surface is smooth, as if varnished - the so-called penicillin tongue. With an allergy to tetracyclines, the tongue is rough and covered with a brown coating.
Common toxic-allergic stomatitis is manifested by various signs and affects all the mucous membranes of the oral cavity. Their symptoms are generally the same: burning, itching, insufficient amount of saliva, soreness in the mouth during eating and talking.
Systemic toxic allergic diseases
Lyell's Syndrome- This is a type of acute severe allergic reaction with a predominant lesion of the skin and mucous membranes, as well as internal organs.
As a rule, this syndrome develops when taking certain medications, especially often antibiotics, sulfonamides, barbiturates. The disease is manifested by death (necrosis) and detachment of all surface layers of the skin in separate areas.
The disease begins suddenly, almost immediately after the next administration of a certain drug. The body temperature rises rapidly to 39 - 40 ° C, weakness, malaise appears, and a sore throat is sometimes possible. Large bright red spots on the background of edema and deep bubbles appear on the skin and mucous membranes. The defeat occupies vast areas of the skin and resembles a burn. After the appearance of skin lesions, the condition of patients worsens: the temperature is kept at high numbers, the patient loses his appetite, sleep is disturbed, he is tormented by headaches. Bubbles burst, exposing large bleeding surfaces. Skin lesions can reach about 90% of its entire area. In this case, such an poisoning of the body occurs with the decay products of its tissues, which can cause toxic damage to the heart, liver, kidneys, and nervous system.
Exudative erythema multiforme- This is a disease of the skin and mucous membranes, which is characterized by a variety of emerging defects.
This disease begins acutely, but then becomes chronic and lasts for years with periodic exacerbations.
Sometimes the disease is manifested by isolated defects of either the skin or the mucous membranes, but more often they are affected simultaneously.
The disease begins suddenly with chills and fever up to high numbers. General weakness, headache, dizziness, pain in muscles and joints are noted. After 1 - 2 days, lesions of the skin and mucous membranes join.
Bluish-red spots appearing on the skin of the face, neck, hands, forearms, feet and legs are bluish-red, protruding above the surface of the skin, rounded. After some time, the central part of the spots sinks and acquires a persistent bluish tint, and the marginal zone remains elevated and retains a red color. In the center of some spots, bubbles may form filled with a cloudy yellowish or bloody liquid. Bubbles burst and crusts form in their place. The appearance of spots on the skin is accompanied by itching and burning.
The defeat of the oral mucosa is manifested by the appearance on the surface of the tongue, mucous membrane of the cheeks, lips, palate of the vast areas of redness and swelling. Against this background, bubbles appear containing turbid liquid, which quickly open. In their place are superficial defects of the mucous membrane (erosion), covered with a whitish coating. Erosions can merge with each other, forming extensive defects of the mucous membrane.
The development of these changes in the oral mucosa is accompanied by intense pain and severe soreness when touching the tongue or food. Therefore, the nutrition of such patients is very difficult. In addition, these changes cause increased salivation in the patient, an increase in nearby lymph nodes.
Pathogenic bacteria can enter the erosion and cause purulent inflammation, ulceration, and then scarring. An exacerbation of the disease occurs with every contact with an allergen.
Stevens-Johnson Syndrome(or a malignant variant of exudative erythema) is a disease of an allergic nature, which is characterized by multiple rashes on the skin and mucous membranes. It occurs almost immediately after contact with an allergen and is characterized by a rapid course. The body temperature rises sharply to 39 - 40 ° C, sometimes with chills. Severe weakness, weakness, and headache appear. Large bright red spots with clear boundaries appear on the skin of the trunk and extremities (often in symmetrical areas), as well as areas of edema, in the area of \u200b\u200bwhich the upper layers of the skin exfoliate and bubbles form. They are filled with muddy contents, and the skin around the edges acquires a bluish tint.
Bubbles appear on the mucous membranes of the mouth and nose, genitals, which burst after a few days. After this, bleeding surfaces are exposed, surrounded by scraps of skin along the edge, which was the cover of the blisters.
A rash may appear on the skin, which is a multiple hemorrhage. Changes occurring on the skin are accompanied by symptoms of general severe poisoning of the body. Body temperature is kept at high numbers, weakness, dizziness, headaches and muscle pain, and sometimes cramps, are noted. The course of the disease can be complicated by nosebleeds, purulent inflammation of the conjunctiva and cornea, as well as cardiovascular and respiratory failure.
Aphthous stomatitis- This is a lesion of the oral mucosa of an allergic nature in the form of the formation of special defects on it - the so-called aft. This disease proceeds for a long time, for years, with periodic exacerbations and attenuation. Aphthous stomatitis occurs more often in women than in men.
After contact with an allergen, which can be some food products, drugs, house dust and other substances, defects (aphthae) appear on the mucous membrane of the inner surface of the cheeks and lips, tongue, soft palate, initially shallow, in the form of erosion, but can deepen to the formation of ulcers. Sometimes these changes are preceded by discomfort in the oral cavity - burning, soreness when touching the tongue or pieces of food. Aphthae are areas of damage to the surface layers of the oral mucosa of a round or oval shape, surrounded by a rim of reddened, inflamed mucosa. They can appear in different numbers - from single to multiple. Their surface is covered with a whitish coating. In mild cases, aphthae independently heal after 5 to 7 days without leaving scars.
Sometimes aphthae deepen and ulcers of a rounded shape are formed, with a diameter of 0.5 to 3 cm. They are also surrounded by a zone of reddened mucosa, have raised edges and a grayish or yellow bloom, and the bottom resembles volcanic craters in shape. Sometimes they merge with each other, forming more extensive damage to the mucous membrane. The sores are very painful, sometimes so much that they prevent the patient from eating normally, conducting oral hygiene and even talking. Gradually they heal with the formation of scars. With this disease, the general condition of the patient is not violated, body temperature remains normal.
The course of the disease is chronic, with periodic exacerbations. The severity of the disease depends on the frequency of exacerbations and the type of damage to the mucous membrane. In a mild course, exacerbations occur 1–2 times a year in the form of the appearance of single aphthae, with an average of every 2–3 months with multiple aphthae and ulceration; in severe cases, changes in the oral mucosa are observed almost constantly and are significantly expressed.
Behcet's Syndrome- This is a combination of several specific symptoms: periodically occurring aphthae on the mucous membrane of the oral cavity and genitals, as well as eye damage.
This syndrome was first described by Turkish dermatologist Behcet, by whose name he was named. Behcet's syndrome more often occurs between the ages of 20 - 30 years equally often in representatives of both sexes. The exact reasons for its appearance are not fully understood.
Behcet's syndrome is characterized by a long chronic course with periodic exacerbations and remissions (periods of improvement), which can last up to several years. However, the general course of the disease is unfavorable for the patient, since each subsequent exacerbation proceeds more and more severely.
A mandatory sign of Behcet's syndrome that occurs in the early stages of its development is defects in the oral mucosa (aphthae). In their appearance, they practically do not differ from aphthae with recurrent aphthous stomatitis. They are distinguished by severe soreness and often exist for a long time, gradually healing with the formation of rough scars. The number of aphthae can be different in different patients - from a few to a count that cannot be counted.
The appearance of rashes on the skin and mucous membranes of the genitals (penis, scrotum, labia) is characteristic. Rashes are formations similar to aphthae, dense to the touch, rising above the surface of healthy skin or mucous membrane, which then turn into painful ulcers, the bottom of which is covered with a yellowish coating.
On the skin of patients with Behcet's syndrome, rashes of the type of nodular or multiforme exudative erythema often appear.
In many patients with Behcet's syndrome, characteristic eye damage occurs. Sometimes it even becomes the first sign of a disease. Initially, the patient is worried about severe photophobia, sharp pain even in ordinary daylight. Then there are changes in the internal structures of the eye, which can lead to an irreversible decrease in visual acuity up to complete blindness.
Over time, aphthous rashes can spread to the mucous membranes of the respiratory system, digestive tract, damage to other internal organs, joints, blood vessels and the nervous system.
With Behcet's syndrome, there is a very characteristic sign: the slightest damage to the skin, for example minor household injuries (scratches, abrasions), intradermal injections cause the appearance of pustular rashes.
Sjogren's syndrome- a condition that can accompany the course of autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, some diseases of the liver and gall bladder, diffuse diseases of the connective tissue (systemic lupus erythematosus, scleroderma, dermatomyositis, etc.). Sjogren's syndrome is characterized by the defeat of the so-called exocrine glands of the human body, i.e., they release their products on the surface of the body or in the lumen of the body cavities. First of all, in this condition, the lacrimal and salivary glands suffer. In addition, Sjögren’s disease is distinguished - a disease that itself refers to diffuse diseases of the connective tissue, but manifests itself in general in the same way as Sjogren's syndrome.
The disease is named after the Swedish ophthalmologist Sjögren, who first described the symptoms listed.
In most cases, Sjögren’s syndrome affects women around the age of 40.
The most frequent and often the first manifestation of a syndrome or Sjögren’s disease is a decrease in the amount of tear fluid produced by the eye, which adversely affects the state of the organ of vision. Patients complain of a burning sensation, itching, sand, a foreign body in the eyes. The eyelids and conjunctiva of the eyes are often reddened, swollen. White discharge may accumulate in the corners of the eyes. Photophobia gradually appears, vision deteriorates.
The second mandatory sign of the disease is the defeat of the salivary glands. Initially, the patient may be disturbed only by a certain dry mouth with excitement, conversation, physical activity, which disappears with the exclusion of these factors. But over time, the disease progresses, and dry mouth haunts the patient constantly. The salivary glands enlarge and become painful. It is difficult to chew food, especially dry, when talking. Saliva is excreted in the oral cavity in a small amount, it is viscous and cannot moisturize the mucous membrane of the oral cavity and chewed food. At the same time, dry lips appear, in the corners of the mouth, jams may appear. The tongue also becomes dry, cracking, and is often painful. A small amount of saliva produced does not contain a sufficient amount of bactericidal substances and does not wash the oral cavity, therefore, such patients often suffer from stomatitis and multiple tooth decay.
Simultaneously with the appearance of these symptoms, nearby lymph nodes increase - submandibular, cervical, etc.
In addition, often patients are concerned about dryness in the nasopharynx and respiratory tract. Dry crusts accumulate in the nasal cavity, a sensation of sore throat appears, patients are disturbed by a constant dry cough. Often in patients with Sjögren’s syndrome or Sjögren’s disease, decreased sweating and dry skin are noted.
Sjogren's syndrome can be accompanied by constant joint pain and sometimes swelling, but changes in the structure and function of the joints usually do not occur.
Abroad, there are several societies of patients with Sjogren's syndrome. They are designed to support people suffering from this disease. Their emblem depicts an arid desert and a drop of water.
Over time, the disease affects the organs of the gastrointestinal tract, kidneys, liver, and nervous system.
In some patients, the symptoms of the disease are mild, and they almost always feel good, while others suffer very much from this ailment.
The disease proceeds chronically, with periodic exacerbations and improvement.
Diseases, the onset or course of which is associated with allergic reactions of the body
In addition to the allergic reactions themselves of various forms and types, which were described in this chapter, there are others that, by their symptoms, would seem to be completely unlike allergies, but nevertheless having an allergic component in their basis of development. At the same time, an increase in the body's sensitivity to a particular substance can occur at first, as if starting the process, or join in the course of the disease itself, an initially non-allergic nature.
There are a lot of diseases in the development and course of which the allergic component plays a certain role.
These are bronchial asthma, eczema, neurodermatitis, Hashimoto's goiter, post-vaccination encephalomyelitis, serum sickness, tuberculosis, syphilis, brucellosis, fungal and helminth diseases, and transplant rejection reaction. Let's consider some of them.
Bronchial asthma- A widespread disease in the world, which is based on an allergic reaction of the respiratory type.
The course of the disease is chronic, with periodically occurring attacks of suffocation. (For more information about this disease (see section Allergy Forms).
Eczema- a skin disease, the allergic onset of which is certain. Eczema is an inflammation of the upper layers of the skin, which, as a rule, begins already in childhood. Often eczema during life affects people who have had atopic dermatitis in childhood.
Eczema in childhood usually begins with facial skin lesions, although over time it can spread throughout the body. The skin becomes red, swollen, and against this background, in some areas, its outer layers depart from the deep, and bubbles form, filled with a clear liquid. They quickly burst, and in their place surface defects of the skin remain - erosion or small sores covered with crusts. Gradually they heal, and the crusts are rejected.
The described skin changes are accompanied by severe itching, which causes the patient to constantly comb skin rashes. In this case, the risk of skidding into the resulting erosion of pathogenic bacteria with the development of purulent inflammation is high. After purulent inflammation, scars remain on the site of healed erosion and ulcers. The course of purulent inflammation is accompanied by impaired general well-being of the patient, fever, malaise, and headaches. Eczema lasts for years, periods of exacerbation of the disease with the above symptoms and periods of relative well-being alternate.
There are several special types of eczema.
Seborrheic eczemaas a rule, it occurs against the background of a patient with seborrhea - a disease of the skin of the scalp with characteristic peeling.
Trichologists and other specialists cannot determine exactly what causes dandruff. According to one hypothesis, dandruff is a mild form of seborrhea.
With seborrheic eczema, characteristic changes occur not only on the scalp and where there is hair on the body, but also in the natural folds of the skin - in the elbow and knee bends, as well as in the upper chest and back.
On the scalp, certain areas of redness appear, covered on top with yellowish crusts and a lot of constantly tearing off grayish scales. A turbid liquid is constantly separated along the edges of such a focus, which dries up with the formation of new crusts. On the skin of the chest and back, foci of eczema look like yellowish-pink spots, covered with whitish scales, sharply delimited from healthy skin. In the natural folds of the skin, the foci are areas of edema and redness of the skin with deep cracks and weeping. Bacteria can invade foci of this type, causing purulent inflammation.
Microbial eczemadevelops as a transition to the eczematous form of other skin diseases and skin injuries. At the site of injury or, for example, pustular rashes, foci of bright red color appear, covered with crusts. Under the crusts are deep layers of pink skin, on which there are separate sores. From the surface of the sores, liquid is separated in the form of separate drops. Sometimes around the main focus that occurred at the site of injury or rashes, several small bubbles appear. They quickly burst with the formation of the same sores as in the focus itself.
In most cases, allergic skin lesions (atopic dermatitis, eczema, neurodermatitis) develop in early childhood during the introduction of complementary foods, that is, at the beginning of the transfer of a child’s nutrition from dairy products to general ones. The use at this time of some food products, which are allergens, sensitizes the children's body and forms a tendency to allergic diseases.
True eczemacan occur at any age, but for different ages have their own characteristics.
On the skin of symmetrical areas of the body, individual clusters of small vesicles quickly appear on the background of redness and swelling. They soon burst, leaving behind small, moist sores. The appearance of these rashes is accompanied by itching.
At an early age, the appearance of foci on the face, chest, buttocks is characteristic. At an older age, rashes more often appear on the skin of the limbs, in the area of \u200b\u200bthe hands, feet, and forearms. Separated from sores dries in the form of crusts. Gradually, weeping ceases, ulcers heal, foci of rashes peel off with the rejection of large grayish or whitish scales (scaly peeling). However, after some time, the described changes appear again, and the disease becomes chronic.
With exacerbations of chronic true eczema, skin changes appear in places of primary foci, and the skin in this place gradually changes. It acquires a crimson-cyanotic color, compacts, becomes covered with small cracks and peels off. In addition, exacerbations are accompanied by the appearance of lesions in areas of previously healthy skin, so after a few years the patient's skin can be affected almost entirely.
True eczema can affect the skin of the palms and soles. In this case, it is called dyshidrotic eczema. In this case, rashes appear in the form of separate groups of dense vesicles on the background of apparently perfectly healthy skin. The skin around such foci often begins to exfoliate. Bubbles itch, burst, crust, heal, and new rashes appear on areas of previously healthy skin.
Neurodermatitis- another skin disease of an allergic nature, which often affects people who have experienced atopic dermatitis or are prone to allergic diseases.
As a rule, neurodermatitis begins in childhood with the typical symptoms of eczema (see above). On the skin of the face, then the trunk and limbs, the skin becomes red, swollen, multiple itchy vesicles appear. They burst, exposing wet surfaces. The disease is chronic, but in most patients it can be cured before the child goes to school. However, in some, eczema becomes neurodermatitis, which can occur in a limited and widespread (diffuse) form.
Limited neurodermatitis is characterized by the appearance of separate foci of rashes on the skin of the neck, perineum, lower extremities. In some areas of the skin of these areas, there are accumulations of vesicles, which differ little in color from healthy skin, and are very itchy. At the center of such clusters, the skin changes its appearance. It becomes denser, acquires a darker color, the skin relief becomes more noticeable. Itching makes patients constantly comb the affected areas, which contributes to the introduction of a purulent infection and the development of inflammation. Limited neurodermatitis is more common in adults.
Common (diffuse) neurodermatitis is manifested by the appearance of many small itchy vesicles mainly on the skin of the limbs and neck. Bubbles do not appear in the form of separate groups, but form extensive foci.
Severe itching also causes scratching and contributes to skid infection. Over time, the skin in the rash becomes more dense and darker than healthy, the skin pattern intensifies.
The disease proceeds chronically with periodic exacerbations. As a rule, they occur in autumn and winter, and in the warm season neurodermatitis usually disappears.
However, with a long course, even in the period between exacerbations, the patient does not look healthy. The skin becomes dry, peeling, the hair becomes thinner and loses its shine, and the nails become brittle.
Often in patients with neurodermatitis there are other allergic diseases - urticaria, hay fever, bronchial asthma.
Serum sickness- This is an allergic disease that develops in response to the introduction of horse serum or drugs containing it to the patient.
The basis of its development is that the serum contains proteins that are foreign to the patient’s body, to which, in the presence of a predisposition to allergic diseases, an allergic reaction develops.
Typically, symptoms of serum sickness appear 1 to 2 weeks after the first administration of serum, and with repeated administrations, the time of their appearance is reduced to 1 to 3 days.
Horse serum is part of tetanus, diphtheria, anti-gangrenous and other therapeutic serums, it is used to treat certain infectious diseases along with other drugs (antibiotics, antipyretic, general strengthening, etc.).
The disease begins acutely. Body temperature first drops slightly, and then rises to 38.5 - 39 ° C. Local symptoms appear in the form of edema and redness of the skin at the injection site of the serum, the nearby lymph nodes increase and become painful. An itchy rash appears on the skin throughout the body (usually by the type of urticaria, less often in the form of erythema and other types of rashes). Isolated swelling of the eyelids, lips, tongue, or Quincke's edema may appear. Perhaps the development of an asthma attack. Often with serum sickness, joint damage occurs. They become swollen, painful. In severe cases, damage to the heart, kidneys, and nervous system is possible.
At the site of serum administration, ulcers, skin necrosis up to muscle tissue and healing with the formation of a disfiguring scar are possible.
The listed symptoms are kept by the patient for 2 to 3 weeks, and then gradually disappear.
Rarely, serum sickness can occur as anaphylactic shock.
The patient suddenly develops all of his characteristic symptoms, and this variant of the course of serum sickness can end in the death of the patient, if you do not give him emergency care.
BrucellosisIs an infectious-allergic disease of a bacterial nature. A person becomes infected with brucellosis from sick farm animals, therefore, workers of farms and other organizations that are in close contact with animals (milkmaids, cattle, veterinarians, slaughterhouse and meat processing personnel) are primarily at risk of infection. In addition, there is a risk of infection when eating milk and dairy products (unboiled milk, feta cheese) that are not sufficiently heat-treated.
Brucellosis begins as an infectious disease. After 1 to 4 weeks after infection, the signs of the disease gradually appear: increased fatigue, lethargy, fatigue, sleep disturbances. Then the body temperature rises to 38 - 39 ° C. Brucellosis is characterized by large fluctuations in body temperature during the day. In the morning it can be almost normal, but gradually increases during the day and reaches high figures in the evening. Sometimes, on the contrary, the temperature in the morning is higher than in the evening. A feature of this disease is the satisfactory state of health of patients, despite the high temperature. Patients with brucellosis are also characterized by severe sweating. The liver and spleen are enlarged. The causative agent of brucellosis almost always affects the human musculoskeletal system: bones, muscles, joints. Patients are concerned about pain in these organs, which usually occurs randomly, of varying intensity and localization. Inflammation of the joints (arthritis), muscles (myositis), osteomyelitis, lesions of the spine and nerve roots extending from it develop.
Brucellosis can occur in acute, but more often in chronic form. In this case, patients are not only concerned about periodically occurring exacerbations. In their body, irreversible changes occur, caused precisely by the allergization of the body by the pathogen. The musculoskeletal system and the reproductive system are primarily affected.
Long-term chronic brucellosis causes persistent disturbances in the shape, and hence the function of the joints. They are deformed so much that they completely stop working. Patients become disabled precisely because of these violations.
Very quickly, with brucellosis, the organs of the reproductive system are damaged in both men and women. Inflammatory processes develop in the internal genital organs, which very quickly lead the patient to infertility.
Helminthic diseases are widespread among the world's population.
Once in the human body, they penetrate into their "favorite" organs and continue their development and reproduction there. Helminths affect many organs of the human body: intestines, lungs, liver, heart, brain, muscles, organ of vision.
Settling in a particular organ, they disrupt its normal functioning and cause the person to have corresponding symptoms. With intestinal worms, he may be disturbed by a loss of appetite, nausea, weakness, abdominal pain, and stool disorders. Damage to the lungs affects the function of breathing and providing the body with the necessary amount of oxygen. A brain lesion affects the functioning of the nervous system and can manifest itself as headaches and various neurological symptoms, up to seizures, depending on the exact location of the helminth in the organ. Worms, living in the human body, consume ready-made nutrients, extracting them from human blood. Therefore, with most helminthiases, patients complain of weakness, dizziness, palpitations, their skin is pale, that is, signs of blood loss are detected. It occurs in small quantities, but constantly, so in the end a rather significant amount of blood is lost.
Sometimes, especially in countries with a low level of sanitary culture, a person becomes infected with helminthiasis in childhood and lives together with “his” helminth for many decades, and sometimes all his life.


