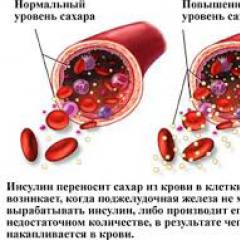
An increase in blood sugar is a major cause. Why does blood sugar rise.
Type I usually occurs with a hereditary predisposition, is detected in childhood, is characterized by rapid development. It is associated with insufficient production of insulin and the accumulation of undissolved glucose in the tissues.
Type II diabetes mellitus, an acquired disease, is caused by tissue insensitivity to insulin produced in full amount. It develops slowly, sometimes for ten years or more. Unlike type I, it is possible that it develops reversibly, and it is extremely important what lifestyle they lead and what people suffering from this pathology eat with high blood sugar.
Norm
Assign with suspected pathology, but sometimes elevated detected completely by accident during preventive examinations. the amount of 3.3 - 5.5 mmol / l is considered, its increase to 6.1 mmol / l is defined as a harbinger of diabetes, and the presence of indicators over 6.1 mmol / l - already developed disease. At the same time, a slight increase to 6.6 mmol / L does not cause concern, but requires observation and control.
For the purity of the analysis, it is important to observe the main rule - until 11 a.m., since after eating, it increases and can show a false result.
What high blood sugar is the norm for people with an established diagnosis? It is believed that the presence of glucose in the blood within the range of 7.8 mmol / L is an acceptable limit for diabetics.
The reasons
An increase in glucose may be temporary and considered a natural process, and may signal impairment.
The most common causes of an increase in blood sugar in an adult and a child that are not a pathology:
- Systematic plentiful food.
- Incorrect analysis.
- Pregnancy and premenstrual syndrome.
- Stress or prolonged psycho-emotional stress.
- Complex fractures, burns, and extensive tissue wounds.
What contributes to the development of type I diabetes:
- Heredity;
- body weight above 4.5 kg at birth;
- acute viral infections (epiparotitis, rubella, measles).
What contributes to the development of type II diabetes mellitus:
- disorders in the thyroid gland;
- improper and irregular nutrition;
- obesity.
Signs
The initial manifestations of hyperglycemia are usually fuzzy and not immediately noticeable, let's try to highlight them.
Early signs:
- dry mouth and tongue, intolerable thirst;
- polyuria (increased urination);
- excessive appetite, while, with type I, a person loses weight, and with type II, on the contrary, the weight rises;
- fatigue, drowsiness, muscle weakness;
- acetone breath (with type I).

Long-term neglect of such conditions leads to pathological changes in the cells of the pancreas.
Symptoms of high blood sugar:
- frequent causeless nausea;
- weakness, drowsiness;
- persistent weight changes;
- disorders in tissue regeneration;
- weakening and impaired vision;
- dry skin and itchy skin.
How to fight
If elevated blood sugar is detected, what should be done to reduce it? There are invariable principles for containing diabetes, thanks to which a person lives a full life. These are: normalization of nutrition, physical activity, drug therapy, self-control.
With diabetes plays a key role. With it, you can slow down and even stop the development of diabetes.
Physical activity regulates minor fluctuations in glucose in the blood, so sports are especially useful in the initial stage of the disease, however, the intensity of exercise should be regulated.
Self-monitoring is carried out using individual devices - glucometers, which are convenient to use in a home environment, measurements are carried out daily two to three times a day.
It is used without fail for type I diabetes (insulin-dependent), in a form not dependent on insulin, drugs are prescribed in an advanced stage or with the development of complications. Most important for non-insulin-dependent diabetes is lifestyle.
Diet
with a high sugar index, it is indicated in medicine as No. 9, this includes:
- whole grain bread (bran, rye);
- low-fat broths and meat (veal, rabbit, turkey), fish;
- vegetables (with the exception of potatoes), which form the basis of the diet;
- skimmed milk products, cottage cheese, sour cream;
- cereals, reducing the consumption of rice and semolina;
- legumes;
- fruits, excluding bananas, grapes;
When diet table number 9 is prohibited:
- natural sugar and sugar-containing products (confectionery, sweets, jams);
- all easily digestible carbohydrates (pastries, pasta);
- fatty, fried, salty, smoked food;
- carbonated sweet drinks, juices of factory production.

Treatment
Depends on the type of diabetes. In the case of insulin-dependent diabetes, the administration of the hormone insulin is mandatory. But it is very difficult to calculate the necessary dose, since the subjective reaction of all people is different. Short-acting insulin injections are prescribed, as a rule, to relieve acute conditions that threaten coma, as well as with the development of post-infectious complications.
In a stable state, the patient is offered oral insulin medications, such as maninil, diabetes, minidiab and others. The tablet forms have a delayed effect, and the effect is manifested when they accumulate in the body.
In the treatment of non-insulin-dependent diabetes, great attention is paid to diet, giving up bad habits, and gymnastics. Often, this is enough to achieve a lasting positive effect. In other cases, the same drugs are used, only the dosages and method of application differ.
Symptoms
In the manifestation of high sugar, there are some differences inherent in a particular category of the population.
Symptoms in women usually look as follows:
- increased thirst provokes frequent urination, the anatomical features of the genitals do not completely get rid of droplets of urine that cause severe itching. Often there are swelling of the face, legs, a sharp decrease in weight, or, conversely, weight gain and obesity, which is resistant to any diet.
Elevated blood sugar in men often goes unnoticed by them in the initial stage. Symptoms of high sugar, such as frequent urination both in the daytime and at night, some disorders of the reproductive system do not prompt the male population to think about an increase in glucose in the blood. Possible pressure drops, weight gain in the male type, accelerated baldness, visual disturbance. Tissue regeneration worsens and a prolonged restoration of the skin is observed.
In a child, with high sugar, you can be suspected of having nocturnal enuresis. The critical age for the formation of diabetes in children is 4 to 11 years, so a symptom such as bedwetting should not go unnoticed. With a steadily elevated glucose level, urine is excreted several times more than in an adult.
Often there are digestive disorders, skin diseases that are difficult to treat. The child drinks a lot, the baby requires frequent attachment to the chest. A mild degree of hypoglycemia can occur without pronounced manifestations, therefore it is extremely important not to ignore the examinations and take all the tests, laid down by age.
Unfortunately, in recent years, cases of diabetes mellitus of the II degree in children have become more frequent, due to improper and irregular nutrition. But such a disease is more difficult to treat, the tablets used by adults do not give the expected result in a child, insulin injections are more often prescribed for children.
We are used to saying "blood sugar", it would be more correct to "blood glucose level." The pancreas produces special hormones insulin and glycogenresponsible for maintaining normal glucose levels. In case of any malfunction in the system, the body lacks energy, fatigue and weakness appear. Such processes are dangerous, primarily due to the fact that during the malfunction of the pancreas, the load on the kidneys increases, which requires an increased fluid content in the body. Then the vessels suffer, because the thickened blood physically cannot get into the small capillaries, and from this irreversible reactions are already going on in all organs and systems.
The norms for women and men do not differ, there is only a slight increase in sugar levels with age. Blood for analysis must be donated in the morning, on an empty stomach. The ideal gap between the last meal and analysis at 10-14 hours. The day before, it is not recommended to eat fatty and fried foods, drink and be nervous.
If all conditions are met, then the glucose level in the blood taken from the finger (capillary) should be 3.3-5.5 mmol / L. if blood sampling was carried out from a vein, then the norm increases by 12% and amounts to 5-6.1 mmol / l. At different times of the day, the indicators will be different, therefore, it is advised to take an analysis in the morning.

Most often, blood sugar levels need to be monitored in order to diagnose diabetes in time - an insidious disease that can go away asymptomatically for a long time, or resemble normal seasonal ailments. This is especially true for those who have relatives with diabetes, the elderly and obese people who lead a sedentary lifestyle.
The glucose level cannot increase simply from scratch, if a person adheres to a proper diet and active lifestyle, then an increase in sugar indicates the presence of diseases.
The main reasons for increasing blood sugar are:
- Excessive consumption of food, especially easily digestible carbohydrates;
- Smoking and drinking;
- Stress and nerve stress;
- Diabetes;
- Diseases of the endocrine system: thyrotoxicosis, Cushing's disease, etc .;
- Diseases of the pancreas, liver and kidneys;
- Taking certain steroid drugs, contraceptives or diuretics;
- Premenstrual syndrome in women.
If the analysis revealed an increased sugar content, the patient was given a drink of the solution and the analysis was repeated after two hours. Sometimes a normal meal before giving blood (a person spent a lot of time on the road to a medical institution and ate) can cause an increase in sugar.

Signs of an increase in blood glucose
Elevated sugar levels lead to hyperglycemia, which can be recognized by the following symptoms.
What explains the increase in blood sugar
Hyperglycemia - This is what the level of increased blood sugar is called. The elevated, as well as the low indicators have characteristic manifestations, which will be described later.
The optimal ratio of sugar in the blood is considered to be from 3.3 to 5.6 mmol per liter, depending on the identification method. The reasons that provoke such a pathological condition may be different. However, over time, they become a catalyst for the formation of signs of an increased blood sugar ratio.
The causes of this phenomenon may equally be:
- diabetes mellitus, which is the most common cause;
- a tendency to overeat, dominating the menu of those that are easily digestible;
- stress situations;
- serious infectious diseases.
This is what affects the process of increasing blood sugar. There is no doubt that in the event of a collision with diabetes mellitus, hyperglycemia will be prolonged and will leave an imprint on the state of most organs and systems.
In more detail it is necessary to dwell on what are in the blood of a person.
What are the symptoms
 Signs of an increase in blood sugar are as follows:
Signs of an increase in blood sugar are as follows:
- intermittent thirst;
- feeling of dryness in the oral cavity;
- itchy skin;
- excessive urination without any pain (may be a sign of low sugar);
- polyuria, or a sudden increase in the ratio of excreted urea;
- nocturia - urine emission at night;
- weight loss;
- migraines and frequent dizziness;
- excessive weakness and increased fatigue;
- prolonged healing of wounds and even scratches;
- frequent infectious diseases (which can also be a symptom of low sugar).
These manifestations make it possible to suspect an increase in blood sugar.
However, the final diagnosis can be made only by determining its ratio using laboratory methods, including using it.
The severity of the manifestations of an elevated level is affected by the severity of the presented condition. Thus, acute hyperglycemia manifests itself more vividly in comparison with chronic. The acute form can form when you use an increased number of carbohydrates on the basis of small doses of insulin.
High sugar is one of the diseases of diabetes.
Chronic development of the disease most often occurs with diabetes mellitus due to its insufficient compensation. In this case, there is a restructuring in the body for an increased blood sugar ratio. Some signs need to be clarified in order to better understand why this ailment is formed and how to deal with it in the future.
Periodically arising thirst is provoked by the fact that glucose is a specifically active substance that attracts water particles to itself.
Thus, with an increase in blood sugar, forced neutralization of fluids from the body occurs. To replenish water costs, the body tries to use the maximum amount of liquid as compensation. This is due to centralized regulatory mechanisms in which the initial impulse is sent to the volumo- and baro receptors.
Migraines, a state of weakness and excessively fast fatigue are a direct result of brain starvation. This is because for the central nervous system (central nervous system) glucose is one of the few ways to get energy.

In the case when its supply to the brain is small, there is a need for restructuring to another method of energy acquisition, which is caused by fatty oxidation.
Lipid oxidation during modification of the blood glucose ratio is able to provoke an increased ratio of ketone bodies. Otherwise, this process is called ketonemia. This explains the formation of the smell of acetone in the air during exhalation. As you know, this is also one of the manifestations of the changed indicator of glucose in the blood.
In energy terms, the negative ability of tissues to heal on the basis of hyperglycemia is also associated with starvation of cells. Slow healing of wounds and scratches under conditions of an increased glucose ratio, which is the optimal nutrient medium for microscopic organisms, has a positive effect on their attachment and further development of purulent processes.
Thus, hyperglycemia is a sharply onset imbalance of bodies in the blood and body, which needs the fastest possible treatment.
Otherwise, serious deviations may occur.
Treatment and prevention
After the diagnosis is made (including for low glucose), a course of treatment is prescribed. For this purpose, it is possible to use:
- diet therapy;
- medical preparations;
- physiotherapy exercises.
The purpose of these therapeutic measures is:
- stabilization of disturbed metabolic processes and body weight;
- preservation or restoration of the ability of patients to work;
- treatment and prevention of vascular type complications.
Diet is a must for all forms of diabetes.
Women should be aware of the symptoms. gestational diabetes - forms of diabetes developing during pregnancy and diabetes as a result polycystic ovary syndrome.
Treating the disease at an early stage will help rule out further complications.
An integrated approach, including a balanced diet and the right choice of products is very important, as it can smooth out or, conversely, worsen the symptoms of the disease.
Symptoms and signs of abnormality
Against the background of increased sugar, a woman may experience the following symptoms: thrush and fungal infections; itching in the intimate area; sexual dysfunction - a high level of glucose for a certain period of time can lead to poor blood supply and / or disruption of the nerve, and lack of orgasm.
 Other symptoms of high sugar include: polydipsia (or unquenchable thirst); polyuria; constant feeling of hunger; fatigue; dizziness; weight loss; blurry vision; slow healing of wounds.
Other symptoms of high sugar include: polydipsia (or unquenchable thirst); polyuria; constant feeling of hunger; fatigue; dizziness; weight loss; blurry vision; slow healing of wounds.
Let us consider in more detail some of the symptoms and manifestations of elevated glucose levels.
Thrush and fungal infections. Vaginal thrush (candidiasis vulvovaginitis) can be a symptom of diabetes. Excess sugar is excreted through the urine, glucose in it can create fertile ground for yeast infections.
Symptoms of yeast vaginal infections include:
- Soreness and itching in the vagina;
- Hyperemia of the skin;
- White curdled discharge;
- Pain during intercourse.
Diabetes mellitus during pregnancy. Gestational diabetes is a specific form of diabetes developing during pregnancy. Its symptoms are the same as in other forms of the disease. Sometimes it is asymptomatic, for this reason women pass an analysis for gestational diabetes between 24 and 28 weeks of pregnancy.
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome. This is a condition in which a woman has a menstrual cycle that is accompanied by a complete absence of ovulation.
Disease associated with high insulin levels in the body, more common in overweight individuals and diabetics.
Proper nutrition with high blood sugar
 A healthy diet reduces the risk of complications such as heart disease and stroke.
A healthy diet reduces the risk of complications such as heart disease and stroke.
A balanced diet should contain at least four nutrients - with fiber, vitamin D.
Omega-3 fatty acids and calcium - working together to help balance blood sugar levels and stimulate weight loss.
Here are some simple rules to follow when designing a menu:
- Feel free to add to your meal. herbs, spices, lemon juice, vinegar and pepper to increase its aroma. Also use a small amount of mustard and seasoning (watch out for their salt content);
- Choose unsaturated fat oils (olive, rapeseed, sunflower, safflower). The saturated fat content in any oil should be less than 1 g per 100 g of trans fats;
- Some patients with high glucose levels are advised snackto containing carbohydrates,between main meals. It depends on body weight, level of physical activity and the type of drugs taken to combat high glucose levels. Suitable snacks may include a small glass of skim milk, sweet diet yogurt, fruits (fresh, canned in their own juice or dried), a slice of whole grain bread;
- Make sure you eat every 3-4 hours;
- Eat at least 5 servings of vegetablesevery day (fresh, canned or frozen). If you feel hungry, give preference to carrots, tomatoes or celery;
- Choose products low salt;
- Drink a lot water (at least 12 glasses per day).
What can I eat with this ailment?
The daily diet should definitely include: vegetables; whole grains (bread, bread); fruits; skim dairy products (up to 2.5% fat content); beans and legumes; diet meat and seafood; poultry (chicken, turkey without skin); fish (also oily).
What should be excluded from your diet?
- High sodium canned vegetables
- Pickles, sauerkraut, pickles (contraindicated for high blood pressure);
- Canned fruits with sugar syrup;
- Jam, sugar jelly;
- Fruit punch, fruit drinks and juices;
- Fried meat (and fatty pieces of meat);
- Lard;
- Hard cheeses of high fat content;
- Deep-fried fish, tofu, meat;
- Fatty dairy products, chocolate shakes;
- Palm oil;
- Carbonated or energy drinks, sweet tea;
- Coffee, sweet tea.
Sample menu for all occasions
We give an approximate menu for the weekconsidering the above products:
| Monday | Tuesday | Wednesday |
| BREAKFAST 1 cup nonfat milk 1 grapefruit 1 cup whole grain cereal MORNING PERKUS1 cup chopped melon DINNER Fried shrimps Bean Salad 50 gr pita 1 cup of milk 2 tablespoons of hummus Celery 1/2 cup brown rice 1 carrot Half banana |
BREAKFAST 1 cup skim milk 1/2 banana MORNING PERKUSFruit granola DINNER Greek Chicken Salad 1 slice whole grain bread Diet vanilla yogurt or cottage cheese (can be sweetened with stevia) 1 cup Brussels sprouts Boiled shrimp 1/2 cup couscous |
BREAKFAST 1 wholemeal muffin 1 cup low-fat milk 1/2 cup blueberry 1-2 slices of low-fat cheese MORNING PERKUS1 apple DINNER 1 cup salad mix Beef Goulash 1/2 cup chopped pineapple
Diet vanilla yogurt (can be sweetened with stevia) Green bean 1 cup skim milk 1 nectarine |
| Thursday | Friday | Saturday | Sunday |
| BREAKFAST 1 cup skim milk 1/2 cup oatmeal 1 dessert spoon of any dried fruit 1 tablespoon walnuts MORNING PERKUS1 kiwi DINNER 1 cup salad mix Eggplant zucchini and pepper ratatouille 1 Slice of low-calorie oat bread with bran 1 cup chopped melon 1 cup blackberry 1 cup skim milk Chicken breast 1/2 cup chopped mango |
BREAKFAST 1 egg 2 slices of low-calorie oat bread with bran 1/2 cup grapefruit 1 cup skim milk MORNING PERKUS DINNER 1 cup salad mix 1 dec. spoon of any dressing Lasagna with spinach and low-fat cheese 1/2 cup apple juice 2 tablespoons of hummus Whole Grain Bun 1/2 cup cooked quinoa grits 1 cup strawberries Pork medallions baked in maple syrup and chipotle glaze |
BREAKFAST 1 cup skim milk 1 whole grain bun 1 tsp peanut butter 1 tbsp jam without sugar MORNING PERKUS1 medium orange DINNER Spiced Chicken Soup 1 cup skim milk 50 gr small pita bread 1 cup chopped watermelon Fat-free vanilla yogurt or cottage cheese (can be sweetened with stevia) 1/2 cup brown rice 1 carrot 1 cup chopped melon |
BREAKFAST 1 cup skim milk 1 plum 1 cup bran cereal MORNING PERKUS1-2 apples DINNER 1 whole grain vegetarian burger 1 apricot 2 tablespoons of hummus 1 cup skim milk 1 cup salad mix Low Calorie Caesar Salad Dressing Chicken Thighs 1/2 cup cooked brown rice |
A few words in conclusion
A properly selected menu, including healthy foods, can gently and accurately lower blood glucose. A balanced diet is a mandatory measure that should become a habit if you want to get rid of the symptoms of high blood sugar and avoid the development of diabetes or gestational diabetes.
There are many different reasons for an increase in blood glucose. The most common and serious is the development in a person of a disease such as diabetes.
Why does blood sugar rise? The causes and factors that contribute to its increase can be very diverse. When conducting a blood test for blood sugar, doctors also pay attention to the age of people.
In a normal healthy person, this indicator should be in the range from 3.8 to 5.5 mmol per liter. The data for pregnant girls is slightly different.
What are the reasons for increasing sugar levels?
Increased blood sugar indicates a malfunction in the normal functioning of the pancreas. It is this body that is responsible for the production of the hormone in the required quantities.
Many people's modern lifestyles can cause blood sugar levels to rise and rise.
The main reasons that contribute to an increase in indicators and exceeding the norm are as follows:
- After eating, glucose levels increase. This phenomenon is considered absolutely normal and within such exceeded limits, the indicators are kept for several hours until all the food taken is assimilated.
- Constant stresses, depression and severe emotional upheaval are also among the factors against which glucose rises.
- It is believed that a normal lifestyle for each person is compliance with the correct mode of rest and physical activity. People who lead a sedentary and inactive life often suffer from the fact that sugar is elevated.
- Alcohol abuse and smoking - bad habits are also included in the reasons why sugar can increase and increase.
- Often the short-term effect is premenstrual syndrome in women, during which the blood sugar tends to increase slightly.
Recent discussions.