Weather phenomena as well. Terms used in predictions
Terms used in short-term weather forecasts
Weather forecast: a scientifically based assumption about the future state of the weather.
Short term weather forecast: forecast of meteorological variables and phenomena for the period from 12 to 72 hours.
The following meteorological values are indicated in weather forecasts: precipitation, wind direction and speed, minimum air temperature at night and maximum air temperature during the day (in degrees Celsius - ° C), weather phenomena.
In the event of occurrence of SN, a hydrometeorological phenomenon that, by its intensity of development, scale of distribution, duration, or by the time of occurrence, may pose a threat to the life or health of citizens, as well as cause significant material damage, a storm warning is compiled. The list and criteria of hazardous meteorological phenomena and combinations of meteorological phenomena related to SN are presented in Appendix A.
Terms used in precipitation predictions
In weather forecasts, terms are used to characterize the fact of the presence or absence of precipitation; in the presence of precipitation, their type (phase state), quantity and duration.
The terms used in precipitation forecasts and the corresponding quantitative characteristics for liquid and mixed sediments are shown in Table 1, for solid precipitation in Table 2.
Table 1
|
Terms |
Precipitations in 12 hours, mm |
|
No rain, dry weather |
|
|
Light rain, light rain, drizzle, drizzle, light rain |
|
|
Rain, rainy weather, precipitation (rain with snow; wet snow; snow turning into rain; rain turning into snow) |
|
|
Heavy rain, heavy rain (heavy rain), heavy rainfall (heavy sleet, heavy rain with snow, heavy snow with rain) |
|
|
Very heavy rain, very heavy rainfall (very heavy sleet, very heavy rain with snow, very heavy snow with rain) |
table 2
For a more detailed description of the expected distribution of precipitation over the territory, the forecast uses the terms in "separate areas" and "places". These terms imply that the expected weather phenomenon or meteorological value will be observed by no more than 50% of the total area.
To characterize the type of precipitation (liquid, solid, mixed) use the term: "rain", "snow", "precipitation". The term precipitation is used only with the obligatory addition of one of the terms given in table 3.
Table 3
|
Terms |
Characteristics of mixed precipitation |
|
Rain with snow |
Rain and snow at the same time, but rain prevails |
|
Wet snow |
Snow and rain at the same time, but snow prevails; melting snow |
|
Snow rolling in the rain |
Snow is expected first and then rain. |
|
Rain turning into snow |
Rain is expected first, then snow |
|
Snow with rain |
The alternation of snow and rain, the predominance of snow |
For the qualitative characteristics of the duration of precipitation, the terms given in Table 4 are used.
Table 4
For detailing the time of onset (termination) of precipitation, it uses the characteristic time of day given in Table 5.
Table 5
Terms used in wind forecasts
Weather forecasts predict wind direction and speed. The wind direction is indicated in the quarters of the horizon (from where the wind blows): northern, southeast, etc. Weather forecasts indicate the maximum wind speed at gusts in meters per second or the maximum average speed, provided that gusts are not expected. In weather forecasts and storm warnings, wind speeds are indicated at intervals of not more than 5 m / s. With a light wind (speed ≤ 5 m / s) it is allowed not to indicate the direction or use the term "weak or alternating directions". If the wind speed values that have reached the value of HW (a dangerous phenomenon) fall within the predicted wind speed interval, then they form a storm warning. The qualitative characteristics of the wind and the corresponding quantitative values of the speeds are given in table 6.
Table 6
Terms used in air temperature predictions
Weather forecasts indicate the minimum air temperature at night and the maximum air temperature during the day, or a change in air temperature during an abnormal run of 5 ° C or more per half a day.
The expected minimum and maximum air temperatures are indicated by gradations at intervals for a point of 2 ° C, and for a territory of 5 ° C. If an abnormal course of air temperature is expected, then indicate its highest (low) value using the characteristics of the time of day shown in Table 5. When using the terms "increase" ("decrease") or "decrease" ("cooling"), "increase "(" weakening ") of frosts, the predicted value of air temperature is indicated by one number with the preposition" to ".
If it is expected that the maximum (minimum) air temperature reaches the values of HW or the temperature values that meet the criteria of HW fall within the predicted interval, then the term “strong heat” (“hard frost”) is used and a storm warning is made. The values of air temperatures related to the criteria for HW are given in Appendix A.
Terms used in weather forecasting
Weather forecasts should include the following expected weather phenomena: precipitation, thunderstorm, hail, squall, fog, blizzard, dust storm, icy frost: ice, sticking (deposition) of sleet on the wires and trees, ice on the roads and snow drifts . In weather forecasts, the term “strong” is used to characterize the intensity of weather phenomena, and “very strong” is used for precipitation if it is expected that the phenomenon will reach the OH criterion in intensity. In other cases, the characteristics of the intensity of the phenomenon ("weak" or "moderate"), except for the intensity of precipitation, are not indicated. In the forecasts of weather phenomena, if necessary, use the terms "strengthening", "termination", "weakening" with the indication "day", "night" or using the characteristics of the time of day shown in Table 5.
Appendix A
LIST AND CRITERIA OF HAZARDOUS METEOROLOGICAL PHENOMENA
|
Phenomenon |
Characteristics of the phenomenon and the criteria for nuclear weapons |
||
|
Very strong wind |
Wind speed (including gusts) 25 m / s and more, on the coast 35 m / s and more |
||
|
Hurricane wind (hurricane) |
Wind speed (including gusts) 33 m / s and more (for continental stations) |
||
|
Sharp short-term (within a few minutes, but not less than 1 min) wind increase up to 25 m / s and more, on the coast 35 m / s and more |
|||
|
Strong small-scale vortex with a vertical axis in the form of a pillar or funnel, directed from the cloud to the surface of the earth (water) |
|||
|
Very heavy rainfall (very heavy rain, very heavy rain with snow, very heavy snow with rain) |
Liquid or mixed rainfall with the amount of precipitation 50 mm or more for 12 hours or less |
||
|
Very heavy snow |
Rainfall 20 mm or more in 12 hours or less |
||
|
Long heavy rains |
Rain with short breaks (no more than 1 hour), with a precipitation amount of 100 or more over a period of 12 to 48 hours or 120 mm over a period of more than 2 but less than 3 days. |
||
|
Large hail |
Hail with a diameter of 20 mm or more |
||
|
Heavy snowstorm |
Snow transfer (including accompanied by snow falling from clouds) by wind with an average speed of 15 m / s and more (in coastal areas with an average speed of 25 m / s and more) and visibility less than 500 m, with a duration of at least 12 hours |
||
|
Heavy dust (sand) storm |
Transfer of dust (sand) by wind with an average speed of 15 m / s and more and visibility of 500 m or less, lasting at least 12 hours |
||
|
Strong icing and frost deposition |
The diameter of the deposition of ice on the wires of the ice machine: ice - with a diameter of 20 mm or more, difficult deposition and / or sticking of wet (freezing) snow - 35 mm in diameter and more rime - sediment diameter of at least 50 mm |
||
|
Hard frost |
Night temperatures: Vladivostok -30ºС and below Southern regions of the region -35ºС and below Western regions of the region -40ºС and below Central regions of the region -43ºС and below Eastern regions of the region -35ºС and below |
||
|
Abnormally cold weather |
In the period from October to March for at least 5 days, the average daily air temperature values are below the climatic norm by 7ºС and more |
||
|
Heatwave |
During 3 days the air temperature was observed: Vladivostok + 33ºС and higher Southern districts of the region + 35ºС and higher Western districts of the region + 37ºС and higher Central regions of the region + 37ºС and higher Eastern districts of the region + 37ºС and higher |
||
|
Abnormally hot weather |
In the period from April to September for 5 days or more, the average daily air temperature is 7 ° C or more above the climatic norm. |
||
|
Emergency fire danger |
Fire hazard indicator is 5 class (10,000 ºС and more according to Nesterov's formula) |
||
|
Frost |
Lowering the temperature of the air or the surface of the soil to values below 0 degrees against the background of positive average daily temperatures during the period of active growing season or harvesting crops, leading to their damage. |
||
|
Heavy fog (strong haze) |
Visibility 50m or less and duration 12 hours or more |
||
|
Combinations of meteorological phenomena related to SN |
|||
|
Combination of phenomena |
Characteristics of the phenomenon and the criteria for nuclear weapons |
||
|
Heavy rain with strong wind |
Rainfall 35-49mm in 12 hours or less with a wind of 20-24 m / s, on the coast 28-34 m / s |
||
|
Heavy snow with icy frost deposits |
The amount of snow is 14-19 mm in 12 hours or less and ice-freezing deposits with a diameter of 17 - 25 mm. |
||
|
Low air temperature with strong wind (for the city of Vladivostok) |
Air temperature -25 ºС and lower with winds of 20 m / s and more |
||
Terms used in long-term weather forecasts
Long-term weather forecast - the forecast for the period from 30 days to 2 years. Long-term weather forecasts include monthly Weather Forecast .
Monthly weather forecast contains the expected values of the anomalies of the average monthly air temperature (normal, above normal, less than normal) and the amount of precipitation (normal, above normal, less than normal) and the expected value of the average monthly air temperature throughout the territory, region, district, etc.
The following characteristics are indicated in the text of the weather forecast:
Air temperature anomaly in the range of 1ºС in gradations:
0 ... + 1 and 0 ... -1 - the norm (about the norm);
1 ... + 2 and + 2 ... + 3 - above the norm;
\u003e +3 - extremely warm (above the norm by more than 3ºС)
1 ... -2 and -2 ... -3 - below normal;
<-3 - экстремально-холодный (ниже нормы более чем на 3ºС).
The expected anomaly of the average multi-year monthly precipitation is predicted in three gradations:
80-120% - the norm (about the norm);
< 80% - less than normal;
\u003e 120% - more than normal.
Climate norm (norm ) - one or another climate characteristic, statistically derived from a long-term series of observations. Most often it is a multi-year average; for example, the average monthly or annual precipitation calculated on materials for a number of years, or the average daily, monthly, annual air temperature also by long-term observations.
The causal relationships of such phenomena are extremely complex, much has not yet received a scientific explanation. While there are no exact answers to such questions, but according to one hypothesis, in many cases of weather-related illnesses, electric fields are to blame: it is assumed that atmospheric ions affect the production of the hormone serotonin, which contributes to the signal transmission between nerve cells. Thus, the electromagnetic fields that constantly arise during charging or discharging the atmosphere can affect human health. In addition, recently it is considered recognized that the complex effects on the human body at the same time several atmospheric factors. That is, discomfort or illness is not caused by any one weather element, but by the general state of the atmosphere. At the same time, different parameters and values may be more significant for different people.
Chapter three What types of meteotropic reactions are distinguished by clinical medicine?
It is safe to call extremely negative the fact that even today, when the development of painful reactions to the weather among many people are scientifically proven, there is no consensus among scientists on this issue. Moreover, definitions in many, and often quite respected sources, suffer from vagueness and are not at all complete. Here is an example of this:
“Weather sensitivity is a deterioration in the state of health and human health caused by the impact of meteorological phenomena. The important natural factors include, first of all, those that affect the thermal regime and fluid balance in the body; atmospheric pressure and aerosols (smog) are also included here. The frontal activity of cyclones with sharp fluctuations in temperature has a particularly strong biotropic effect; along with changes in heat balance, they affect sleep, the body's reactivity and ability to concentrate. Some diseases caused by meteosensitivity, with appropriate susceptibility may occur even before the weather changes. ”
This is a quote from the latest edition of the Big Encyclopedic Dictionary. As you can see, not a word is said about how people suffer from the passage of atmospheric fronts, temperature fluctuations, humidity, pressure, etc. This suggests that even now quite a few researchers stubbornly tend to consider meteosensitivity not as a disease itself, but rather as a sharp reaction of the organism to certain stimuli that appear under various meteorological conditions. That is, it is rather a matter of physical vulnerability, of an insufficient ability of the body to adapt to weather changes. Undoubtedly, the degree of adaptability is very important. And yet, as has already been said more than once, it is the weather (or its change) that undoubtedly creates quite significant changes in the way people feel. However, it is also true that our reactions to weather differ in the intensity of their manifestation. Therefore, those scientists and physicians who closely deal with such reactions created a special classification, according to which three different degrees of reaction to the weather are distinguished. Below is a brief and somewhat simplified description.
So, the first degree - meteosensitivity. It occurs when people respond to an approaching change in the weather with complaints of a general deterioration of well-being. This can be expressed in severe malaise associated with headache, migraine and sleep disorders, as well as palpitations and a significant increase in blood pressure.
Further, according to this classification, should meteoreaction It is expressed in a change of mood and well-being, not accompanied by pain or illness. The researchers described this form of sensitivity as a defensive reflex, a type of acquired early detection system that is needed in order to have time to tune in to changing weather conditions.
Finally, the third, and most severe in its manifestations and consequences, the degree of possible physiological reactions to the weather is meteorological dependence. In this form, chronic patients develop painful symptoms with certain effects of the weather. For example, long-term injuries, healed fractures or stumps after amputation cause significant pain. In chronic diseases of the respiratory tract severe asthma attacks are possible, with coronary heart disease - myocardial infarction.
Actually, there is no doubt that susceptibility to meteorological processes once served as an effective way of preserving and surviving a species. However, the volume of complaints that today makes in connection with changes in the weather, is already clearly a painful reaction. Therefore, these problems and doctors today are engaged in - to a greater extent than meteorologists and climatologists, as it was before.
Chapter Four What are extreme weather events?
It should immediately make a reservation that “normal” weather factors, such as heat, cold, wind or rain, etc., can become extreme in cases where their values exceed a certain threshold. You have probably heard reports of extreme heat in European countries (especially Greece and Italy). In recent years there have been several cases where the heat has become a real disaster on a national scale. Many scientists are inclined to associate this fact with the consequences of global warming and other factors of anthropogenic impact on nature and climate; others dispute this point of view - but the fact remains: nowadays, extreme weather events associated with a critical excess of normal temperatures occur almost daily in the most diverse geographic areas - and their frequency is increasing.
However, there are a number of weather factors that are extreme “by definition”. And not without reason in everyday life, people call them not "extreme weather events", but natural disasters.
Moreover, the majority of such disasters, which are associated with destruction and human casualties, are determined in one way or another by the state of the weather, because they are directly connected with various processes occurring in the atmosphere. Damage caused by the elements often has disastrous consequences on the scale of entire countries and even geographic areas.
In our country, fortunately, some of these terrible weather phenomena are not yet observed. In particular, tropical hurricanes and tornadoes (although tornadoes have become increasingly frequent in recent years). Nevertheless, tropical hurricanes in the Caribbean and Australia, tornadoes over the territories of the United States and Cuba, when the destructive wind, twisted by a funnel, destroys everything in its path, sometimes killing many human lives.
In lower latitudes, destructive tornadoes compete with them, which also affect certain areas of Russia. In addition, in the southern regions are frequent avalanches in the mountains, heavy rains causing mudflows.
In Europe, almost every year there are floods, affecting one or the other country or entire regions. In recent years, England has increasingly suffered from floods.
We now list the weather phenomena, which are called extreme, in order to further analyze their consequences. So, some of these phenomena is caused tropical cyclones. These are areas of very low pressure, the occurrence of which is characteristic of tropical latitudes. When cyclones storm wind forms in cloud masses around the center very low atmospheric pressure. Warm and moist air rises from vast areas for a long time, entraining the air of the surroundings and forming a wind that involves all new air masses; while the pressure in the center continues to fall. Under these conditions, is born tropical cyclonewhich gains destructive power until it moves to a region with a lower temperature, when it is fed with warm moist air. A cyclone, as a rule, carries with it the amount of precipitation that causes strong floods.
Nowadays, a large number of people die in destructive floodswhich now occur in the previously relatively prosperous areas.
Floods arise in cases where the amount of water as a result of, for example, heavy rainfall, begins to dramatically exceed the carrying capacity of rivers in the area. Thus, floods are somehow related to the weather. They can cause not only heavy rains (such floods are typical both for low latitudes, where they are annually, and for areas with a monsoon climate), but rapid melting of snow (which is more typical for middle latitudes). Finally, in coastal areas, flooding can be the result of a powerful wind driving masses of sea water to the coast.
Besides floods, brought by a cyclone, in its lane for several hours blows hurricane windand if it affects populated areas, the consequences are difficult to predict.
It is even more difficult to predict such an extremely destructive phenomenon as tornado. So called the spinning column of air, stretching from the thunderstorm cloud to the ground; the wind reaches speeds of up to 320 km / h. a few minutes is enough for this phenomenon to completely devastate the vast terrain. Tornado common in Asia, and on sea islands, and in Australia, but the absolute primacy belongs to the United States. This terrible phenomenon every year takes human lives.
It should be noted that although the wind of tropical cyclones is not as strong as with a tornado, it captures much larger areas, often reaching from 500 to 1600 km in diameter, and the zone of hurricane wind reaching a speed of 250 km / h can cover areas more than 50 km In this case, cyclones carry a huge amount of water, which causes not only floods, but also mudflows.
Boarded - This is one of the most dangerous natural disasters; they are characteristic mainly of mountain regions (for our country, this is the Caucasus). Sel It is a powerful stream of dirt and stones that it carries with it, rushing down the mountain slopes or the beds of mountain rivers. In the mountain gorges there are frequent blockages of stones, rubble, pieces of ice, as well as snow dams. With the rapid melting of the glacier, water may accumulate in front of them, forming a lake. Under the pressure of all coming from above the meltwater, the obstacle in its path can not stand and rush down. Then the stream (and its height can be tens of meters) rolls uncontrollably into the lowlands, absorbing new masses of stones and dirt along the way, until it breaks out of the gorge into the valley. Here its speed gradually decreases until the mudflow stops completely. But if a settlement is in the way of a mudflow, human sacrifices are very often the consequences, not to mention the enormous economic and material damage.
If floods, hurricanes and mudflows can be predicted with a relatively high probability, then such an extreme phenomenon as tsunamialmost unpredictable. Tsunami - these are huge waves, sometimes more than 10 meters high. They can be considered a non-meteorological phenomenon in the full sense of the word, since the most frequent cause of a tsunami is underwater earthquakes in the world's oceans. However, phenomena very similar to tsunamis can also be observed when passing a tropical cyclone, when water rises 3 to 4 meters in its center, which increases the height of coastal waves several times.
Finally, one should mention such a potential source of danger as severe thunderstorms. Although thunderstorms are one of the usual weather phenomena, they carry a rather dangerous potential, which, unfortunately, does not so rarely become realized. What is the reason? First of all, with heavy wind. There are several options for the occurrence of thunderstorms, but the first and indispensable condition is a certain instability of the atmosphere at this point in time. Further, the decisive role is played by air masses: first of all, the air must rise quite considerably, and subsequently - cool and condense. Thus, during the passage of a thunderstorm, the vertical movement of air directly under the cloud can generate strong gusts of wind. In addition, the precipitations sometimes form very strong descending air flows, but the main danger associated with thunderstorms is lightning electrical discharge of millions of volts. In addition to those cases when, when hit, lightning injures and kills people, it can also cause fires and man-made disasters.
Chapter Five What are the health effects of extreme meteorological factors? How does this relate to weather sensitivity?
Let's start with the floods. They can be considered as part of a natural process that changes the shape of the earth's surface. And in this case, to a certain extent, their beneficial effect at the level of ecological and biological systems is undoubted. In particular, regular floods of the affluent rivers of our planet saturate huge areas with moisture (the most striking example is the Nile Delta in Egypt, where one of the most ancient civilizations of the Earth originated), this makes the soil extremely fertile, which is why today the deltas of large rivers are usually , the largest agro-industrial areas with a highly developed agricultural crop. But in this case, the authorities of these areas have to take measures against floods to ensure the safety of the population. Because floods still remain an extreme weather factor, and they can cause great damage, with the most important - with far-reaching and long-lasting negative consequences.
By the way, when a person erects dams, embankments or canals, and all these are the most widespread measures of protection from the elements everywhere - often the damage caused by floods is intensified. For example, artificially raised banks of the river do not release water until it exceeds their boundaries, and without it the water would quickly leave the river, naturally lowering its level. Now the water for days and weeks accumulates within the borders of the stone embankments. This, as well as the artificial straightening of the river bed, leads to the fact that the flow velocity increases and even the calmest rivers can become turbulent. If we add to this the drainage of the coastal area, coupled with its covering with asphalt or concrete, which does not allow water to sink into the ground, then it becomes quite clear why the threat of sudden floods has increased everywhere.
Some areas of the globe are highly susceptible to monsoon rains, and often the population does not take natural protection measures seriously enough. For example, the terrible floods memorable to everyone in Malaysia, Sri Lanka, Bangladesh probably would not have been so devastating if the forest had not been completely cut down on the mountain slopes and hills. In addition, the short-sighted policy of agricultural structures to replace the natural plant environment with an artificial one also undoubtedly increased the terrible effect of these floods.
But floods under any conditions are capable of becoming powerful destructive factors, if the water level dramatically exceeds the average values. What can contribute most to this? It:
◦ Heavy rains, especially in areas covered by monsoons, overflow with tributaries of rivers. As a result, water rises in the main channel (river floods). A heavy rainfall, for example, during a short but powerful thunderstorm can cause a sudden flood in almost any terrain.
◦ Storm tides during the period of powerful cyclones - while this is not only about tropical latitudes - can raise the sea level so that coastal land will be flooded.
◦ Dams, that is, barriers to water created for people can block its path, causing powerful floods in the upper reaches of the river, although its course is not too wide there. Such floods are also often sudden, and therefore destructive.
◦ In spring, the broken ice of the river can accumulate in narrow passages, creating ice jams that can cause powerful flooding when the weather changes rapidly to warmer.
◦ Any artificial reservoirs can cause terrible floods if, for one reason or another, their walls, dams and locks are destroyed.
◦ Nor can we mention the tsunami when underwater earthquakes or volcanic eruptions can cause monstrous heights of waves that fall on coastal areas. At the same time, depending on the geographical features of the region, tsunamis in some cases are capable of penetrating inland to several kilometers (!)
◦ While this did not happen, which means that the issue is considered controversial - and yet, more and more prominent scientists today are talking about the danger of polar ice caps flooding as a result of global warming. If this happens, the increased sea level will flood many islands and coastal areas - in Europe, in America, and in Asia.
Death and destruction - and in vast spaces, and often kills thousands and thousands of people. Here is the first effect of a powerful flood. This is very tragic, but this is only the first effect - we are talking here about the long-term consequences.
And in this regard, the floods bring us not only death and destruction, they are undoubtedly the cause of the spasmodic increase in the incidence of many diseases, in the first place - infectious, if we talk about the long term. How does this happen? The simplest example: a population without shelter is seeking refuge in improvised shelters, in which conditions are usually unsanitary. Often, there is also a lack of quality, even just enough clean, fresh drinking water. In the dirty water is a lot of pathogenic bacteria, and if the weather is hot, it leads to their rapid reproduction. Here are just some of those infectious diseases, outbreaks of which may be caused by flooding, which has now been scientifically proven and cannot be doubted. It:
◦ Malaria. Spilled water - the vast space for breeding mosquitoes and other blood-sucking insects - which, as you know, are carriers of this disease.
◦ Typhoid fever, one of the most acute and serious infectious diseases, is spread through contaminated water and food. Moreover, the most effective means of struggle - elementary adherence to sanitary and hygienic norms - after a flood, like any natural disaster with many victims - is often simply impossible to use for almost understandable reasons.
◦ Cholera - its epidemics would seem to have won a long time ago, but under conditions of lack of clean water, food, and an acute shortage of necessary medical care (after all, after a natural disaster, huge reserves are usually mobilized, and even they are not enough) - outbreaks of this disease are possible .
◦ Dysentery is the real scourge of the population affected by floods, because the pathogens of this disease, the so-called Shigella, multiply most rapidly in stagnant, dirty, especially warm, water.
It is absolutely necessary to note here that the flood victims and those who have undergone enormous hardships, who are, moreover, in a state of extreme stress, have a sharply weakened immune system, which makes them easy prey for pathogens.
And the last - unfortunately, not only microbes are activated as a result of extensive flooding. The water drives rodents, snakes and other animals out of the holes, all of them are in a panic, which makes them very aggressive. Poisonous snakes and various animals can attack humans in search of food; no exception and rats, which, moreover, are also carriers of a whole mass of diseases.
Now let's talk about the wind. A strong wind causes significant damage and directly injuring people and destroying their homes. Meanwhile, even during a fairly strong thunderstorm, the wind can become gusty, then squaler, reaching a speed of 80 km / h and higher. The hurricane wind that has swept through densely populated areas — a kind of air tsunami — overturns cars, uproots trees, tears roofs off houses. Long-term consequences - the abundance of man-made disasters and the difficulties associated with their elimination, given the large number of victims.
In terms of the development of hurricanes, the most dangerous vertical movement of air directly below the cloudy front - it generates the so-called descending gusts of wind. Such hurricanes, squalls and tornadoes are much stronger, their speed can reach 240 km / h.
But strong ascending air flows are dangerous in that they are able to keep hail in the clouds until the hailstones have reached a considerable size, which makes hailstorm extremely destructive. The long-term consequences are a massive loss of crops, which in the future often means food problems, and for the poorest countries, just hunger.
Wind during thunderstorms can be unpredictable nature of sudden gusts (squalls), which carry a huge destructive potential.
Extremely strong wind annually brings huge losses, in whatever form (hurricane, tornado, storm squalls, etc.) it does not manifest itself. And the consequences have to be eliminated for a long time. If a hurricane happened in winter, whole cities or densely populated areas can remain without electricity for a long time, the number of diseases associated with hypothermia increases dramatically.
No matter how tragic, each year extreme weather factors take tens, hundreds, thousands of human lives. However, if we talk about long-term consequences, two troubles come to the fore, indisputably: destruction caused by the economy and a very significant increase in the incidence (of one or another class of pathologies) of the population.
At the same time, in economic terms, it is often difficult even to immediately assess the so-called secondary losses - this means temporary provision for shelter and food for people affected by the disaster, the cost of repairing damaged buildings and utilities, and much more.
But how does all this relate to meteopathogenic reactions, weather dependence, the reader may ask. The answer is: in the most direct way, although at first glance this does not seem so self-evident. The fact is that the number of extreme meteorological phenomena is growing all over the world today - this is proved by statistical data. Meanwhile, any extreme effects weaken the human immune system in the first place. But it is she who is responsible for the development of the degree of meteosensitivity. In other words, if the passage of several powerful cyclones and anticyclones during one winter or summer simply increases the number of weather sensitive people, then after extreme meteorological phenomena the number of such people in the affected area doubles as a minimum. This is the data of the WHO subcommittee specially created at the UN on extreme weather events, they can be found in the press and on the Internet. In addition, WHO publishes official bulletins annually, and data on extreme events, their immediate and long-term consequences are certainly present in such bulletins.
Thus, the relationship between the long-term effects of extreme weather events or exposure factors and public health is obvious, and one of the important components of this connection is the annually observed increase in the incidence of weather sensitivities in all regions and countries of the world.
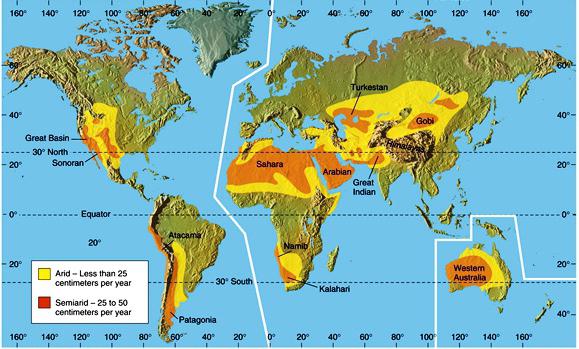
Atmospheric precipitation called water droplets and ice crystals falling from the atmosphere to the earth's surface.
Precipitation is visually divided into light, moderate and strong. The following types of precipitation are distinguished:
1.Solid - snow, snow pellets, snow grains, ice pellets, freezing rain and hail.
2.Liquid - rain, drizzle.
3.Mixed precipitation - wet snow.
According to the physical conditions of formation and the nature of precipitation, precipitates are distinguished: headaches, storm showers and drizzling.
Precipitation - characterized by moderate, little varying intensity. They cover at the same time large areas and can continuously or with short breaks last for several hours and even tens of hours.
Rainfall - are notable for the suddenness of the beginning and the end of the fallout, sharp fluctuations in intensity and relatively short duration. Usually they cover a small area. In summer, it rains so much, sometimes with hail. Summer rainfall is often accompanied by thunderstorms. In winter, heavy rainfall is a heavy snowfall, consisting of large flakes of snow.
Drizzle - it can be drizzle, the smallest snowflakes or snow grains.
Hail It originates like rain - at first it is water droplets. But before they fall to the ground, the wind picks them up and lifts them into the cold air. There they manage to freeze and again begin to fall, colliding along the way with raindrops floating in a cloud, which stick to them and freeze. Sometimes such an ice nucleolus manages to repeatedly rise and fall down again, and each time a new layer of ice builds up on it. The hailstones become larger until finally they fall to the ground. If you split such a gradient, you can see how on the nucleolus, like tree growth rings, ice layers grew.
A hailstone can reach the size of a chicken egg and in the fall cause considerable damage to crops, flowering trees, breaking stalks and knocking down buds. From the fields, beaten by hail, it is difficult to collect even the remaining crop. Large hail can also damage homes, cars, and even cause death to people and animals.
The frequency of hail falls is different: in temperate latitudes, it happens 10-15 times a year, at the equator on land - 80-160 times a year, since there are more powerful ascending flows. Over the oceans hail falls less frequently.
In our country, developed methods for determining the city-hazardous clouds and created services to combat hail. Dangerous clouds are "shot" with special chemicals, preventing the rain from turning into hail.
Sleet can be observed at a positive air temperature close to 0 ° C, when the snowflakes falling from the clouds slightly melt or when rain falls with the snow and the snowflakes merge into flakes. Flakes of such heavy or torrential wet snow stick to trees, poles, wires, etc. and, reaching dangerous sizes and weights, cause serious damage to certain branches of the national economy.
Ice - deposition of ice on the surface of various objects, due to the deposition and freezing of drops of supercooled rain, drizzle or fog at a negative temperature in the surface layer of air. The thickness of the deposits is usually a few millimeters, and in some cases can reach 20-25 mm or more.
Fog
Fog and haze they are the result of condensation of water vapor in close proximity to the earth’s surface, i.e. in the surface layer of the atmosphere. Fog called a set of suspended in the air water droplets or ice crystals, worsening the meteorological visibility range to values less than 1 km. With a visibility of 1-10 km, this set is called haze.
Depending on the visibility range, the intensity of haze or fog is estimated by the following gradations:
Weak haze (2-10 km);
- Moderate haze (1-2 km);
- Light fog (500-1000 m);
- Moderate fog (50-500 m);
- Heavy fog (less than 50 m).
At positive temperatures, the fog consists of water droplets with a radius of an average of 2-5 microns, and at negative temperatures - of supercooled water droplets, ice crystals or frozen droplets. Water droplets that form a haze have a radius of less than 1 micron. Visibility in a fog depends on the size of the droplets or crystals that form it and on the water content (amount of liquid or solid water) of the fog.
According to the physical conditions of education, fogs can be divided into the following types:
1. Cooling mists - formed as a result of lowering the temperature of the air adjacent to the earth's surface. This can occur as a result of: radiation - cooling the soil surface (radiation mists); warm air leaks onto a colder surface (advective fogs); air rise on a hill or mountain slope (mist slopes)
2. Non-cooling mists - evaporation fogs and offset fogs. Fogs of evaporation are observed in cases where the temperature of the water surface is above the temperature of the surrounding air. Their formation is due to the cooling and condensation of steam entering the air from the water surface. Displacement mists are formed when two air masses are mixed, having different temperatures and containing water vapor, close to the saturation state.
3. Fogs caused by human activity - urban and frost (kiln) fogs, as well as specially created artificial fogs, for example, to combat frosts.
Rime - deposition of ice crystals on various objects (antennas, tree branches, etc.) at low air temperature, mainly from their windward side. It is the result of the sublimation of water vapor in a fog or the freezing of drops of supercooled fog.
Clouds
Cloud called visible accumulation of condensation products or sublimation of water vapor at a certain height.
Precipitation falls out of the clouds, thunderstorms arise in them, they affect the influx of radiant energy to the active surface and thus the temperature regime of the soil, water bodies and air. Clouds have a large variety of forms and physical structure.
Depending on the conditions of formation, all clouds are divided into three classes:
1. Heap-like - highly developed vertical clouds, but having a relatively small horizontal extent. They are formed as a result of intensive ascending (convective) air movements.
2. Wavy - layers of clouds having a large horizontal extent and the appearance of "sheep", shafts or ridges. They are formed as a result of wave movements in the atmosphere.
3. Laminated - layers of clouds in the form of a continuous veil, the horizontal extent of which is hundreds of times greater than the vertical dimensions. They are formed as a result of slow, smooth upward movements of air.
Wind
Windi.e. the movement of air relative to the earth’s surface is due to the unevenness of atmospheric pressure at different points in the atmosphere. Since the pressure varies vertically and horizontally, the air usually moves at a certain angle to the earth's surface. But this angle is very small. Therefore, the wind most consider the horizontal movement of air.
Wind speed and direction characterize the overall movement of the air flow as a whole. But in moving air due to friction on the earth's surface, as well as the unevenness of its heating, there is always turbulence.
The nature of the movement of air, due to individual shocks and gusts, sudden intensifications and weaknesses of the wind, continuously following each other, is called gusting wind. Measurements show that "elementary gusts", i.e. intermittent increases and decreases in wind speed are on average 3 m / s, and their duration is tenths of a second.
A sharp short-term increase in wind in a limited area is called squall. Wind speed at squall increases to 30 m / s and more, and the duration of the squall reaches several minutes.
Tornado - A whirlwind with a vertical or curved axis that occurs during a squall or thunderstorm and has a very high rotational speed. Wind speed in tornado often exceeds 50-70 m / s, which causes catastrophic destruction. The appearance of tornadoes is associated with strong instability in the lower layers of the atmosphere.
Dry wind - wind at high temperature and low relative humidity. In dry winds, the temperature is always above 25 ° C (often rises to 35-40 ° C), relative humidity is below 30%, wind speed is more than 5 m / s (often reaches 20 m / s). Hot dry wind is one of the meteorological phenomena most unfavorable for the national economy. Under its influence, evaporation increases, the water balance of plants is disturbed, the water level in rivers decreases, and so on.
General snowstorm It represents the transfer of strong wind falling and / or raised from the underlying surface of the snow almost in a horizontal direction, accompanied by vortex movements. In this case, it is not always possible to determine whether this is falling snow or snow that has been lifted from the underlying surface.
Blowing snow It represents the transfer of a strong wind raised from the underlying surface of dry or freshly fallen snow. In this case, the transfer of snow occurs in the air layer with a height of up to 5 m.
Drifting snow - transfer of dry or fresh snow by a strong wind directly above the underlying surface in an air layer up to 1.5 m high.
Other atmospheric phenomena
Thunderstorm - an atmospheric phenomenon, in which electrical discharges appear in the clouds or between the cloud and the earth’s surface - lightning accompanied by thunder. As a rule, a thunderstorm forms in powerful cumulonimbus clouds and may be accompanied by squalls, heavy rainfall and hail. It is observed mainly in the warm season, but sometimes in winter.
Rainbow is an optical phenomenon in the atmosphere due to refraction, diffraction and reflection of light from water droplets. The outer part of the rainbow is colored red, the inner part is purple. The remaining colors are arranged in a rainbow according to the wavelengths of the sun's radiation spectrum. The color, width and intensity of the rainbow are not always the same. Often, from the outside of the main rainbow, there is a secondary rainbow with a reverse alternation of colors, concentrating with respect to the main one.
Halo - the phenomenon associated with the refraction and reflection of light from ice crystals and is formed mainly in pinstripe clouds. Halo has the appearance of light colored circles or arcs, light pillars or spots around the sun or moon. This optical phenomenon has the brightest color of a reddish color and a clear border on the inside. To the outside, the brightness decreases and the circle gradually merges with the gray or whitish color of the sky.
 Today we will talk about climate change that can occur in 2018, as well as how they can affect the events in the world.
Today we will talk about climate change that can occur in 2018, as well as how they can affect the events in the world.
There are many hypotheses about the direction in which climate is changing, and many believe that global warming is occurring due to man-made influence. Along with this, there is an assumption about the general destabilization of atmospheric phenomena, and from our point of view this opinion is more justified. Some scientists believe that destabilization is associated with human activity, in particular with the emission of carbon dioxide leading to the melting of glaciers, and as a result - to the redistribution of vaporous water in the atmosphere, which manifests itself in active air currents. Other experts suggest that the same technogenic influence should lead to a greenhouse effect, that is, a general increase in temperature. However, it can be assumed that climate change is not at all connected with the influence of society, and all these phenomena are created by the forces of nature itself.
Indeed, the emission of aerosols and carbon dioxide into the atmosphere is not so great as to raise the global temperature by several fractions of a year. The technogenic civilization simply does not have such a volume of energy as to lead to global consequences. Similarly, the industry is not able to lead to the destabilization of natural processes, since the impact of technology in different parts of the Earth should be similar and not lead to different consequences. Consequently, nature itself creates a certain failure within itself, which leads to a deviation of weather phenomena from the norm.
One may ask: why should the natural system organize such oscillations?
They are needed in order for natural phenomena to become more diverse and to be able to manifest a greater range of properties, which under normal conditions are reduced. This concerns not only the processes in the atmosphere, but also geological phenomena occurring inside the Earth, as well as the development of biological organisms. As long as the energy in nature circulates in standard rhythms, then its external manifestations are monotonous. But if the cyclical nature is broken and constant drops are observed, then any phenomenon and the organism has to find new approaches to ensure its existence. In order to adapt to the changing conditions, any process becomes more active, that is, it accumulates internal energy which at any moment is able to direct to its transformation. Therefore, air currents become more active, so they are easily able to change their direction.
The same will begin to be observed in wildlife - organisms will find new ways of energy storage, and at first this will manifest itself in an increase in their viability and ability to adapt to the fluctuations of the weather. Over time, such physiological flexibility will lead to the manifestation of abilities that will help plants and animals to easily adapt to changes in the external environment. Plants will learn to change the shape and size of the leaves in a few months, which may be necessary to change the rate of evaporation of moisture from the surface of the leaf. The color of the leaves may also change to adjust to the features of solar radiation, which has become more active and rigid in recent years. In order to absorb shorter wavelength radiation, plants can begin to incorporate new photosynthetic substances into their tissues, and as a result, they will acquire a multi-colored color. At the same time, the natural system, trying to protect its environment from excessive exposure to sunlight, will shield radiation by forming a dense layer of clouds.
As a matter of fact, such an effect has already begun to occur, and therefore in recent years cloudy weather has become a particularly frequent occurrence. Because of this, most plants will have to adapt more, not to bright sunlight, but rather to its lack. Therefore, the composition of the leaves will appear substances capable of absorbing light radiation especially effectively, and a constant experiment is likely to occur in order to more successfully adapt to changing external conditions.
In general, plants will need to expand the range of their capabilities, learning to adapt to both unusually hot and dry weather with a large abundance of light, and a lack of light and heat, which will lead to the need to save vital energy. It is possible that the issues of lack of resources will be solved by plants through the formation of special rhizomes or other repositories located in the stem and leaves, allowing you to store valuable substances. In order to more actively respond to external events, plants will need to carry out a year-round cycle, that is, photosynthesizing not only in summer, but also in winter. Such changes in the plant world will certainly affect animals, starting with the need to change the color of their body due to a change in the color of the plant cover and ending with a change in the composition of the food of plant-eating animals.
Perhaps the first changes in the physiology of plants and animals will begin to be observed already in 2018, and although they will not be so obvious, in some areas a particularly rapid adaptation will already begin. This will be associated with particularly frequent fluctuations of weather in such a place, as a result of which living beings will also have to learn how to vary their attributes. In fact, nature seeks to temper its people and arranges something similar to a douche when sudden changes in temperature lead to an improvement in blood circulation and immunity.
Such properties of an organism, based on its ability to quickly adapt, are associated with a more rapid flow of its vital energy, when a rapid flow can be directed to the activation of some new quality. If the energy moves inside the body slowly and inertly, then its strength is simply not enough to overcome the internal barriers created in the development process. Such restrictions are most often associated with the body's habit of reacting to external disturbances in a certain way, and in biology such stereotypes are called reflexes and instincts. Under new conditions, a living being needs to be more flexible, so it must have the strength to escape from the internal constraints developed during natural selection. Therefore, creating a lot of fluctuations in environmental parameters, nature forces the body to activate and cancel many of its old programs. Due to this, there is an opportunity to reach a new level of development, when the body can independently conduct its transformation, choosing for itself a new form of existence.
Until now, the signs of most of the inhabitants of nature were mediated by their genetic kinship created during the course of evolution, as well as the pressure of natural selection, forcing them to change the signs only in a certain direction. Now, due to the energy surge in the body, he will be able not only to respond to external influences, but also to approach his abilities creatively, incorporating such characteristics into his structure that will reflect his personal desires. In fact, in each plant and animal its particular character will begin to manifest itself, which will not depend on the species, but will be associated with the needs of the essence that lives in the body of a biological organism. Therefore, it is possible that the destabilization of natural phenomena will lead to the departure of the biological nature from a distinct species structure, and different creatures will begin to freely interact with each other, creating new forms of symbiosis and crossing, creating unique hybrids with new properties.
In general, the species diversity that biologists are observing at the moment is an artificial picture, similar to a still photo, since the previous conditions were extremely stable and did not allow living beings to change. Biological organisms simply did not have an incentive to carry out an internal transformation, and they spent all their excess energy on interspecific competition. Now, in the new conditions, the inhabitants of nature will have to move away from the confrontations, and failures in weather will act like a shock that will turn the body inward in search of a new solution. Such a focus of attention will help each creature to remember its own desires, and the surge of forces that occurred as a result of external activation will help to fulfill these needs.
All of the above is a general trend that will be observed in the coming years, and it will begin to gain momentum in 2018. Those weather fluctuations that became noticeable in 2017 will now become more frequent, and the number of cloudy days may increase as a result of the need for the natural system to screen the hard radiation of the sun. The upcoming winter may turn out to be quite wet, since an abundance of clouds will lead to the creation of a global cyclone in central Russia. However, from time to time northern cold winds will break through to your climate zone, which will set an anticyclone leading to clear and frosty weather.
Most of the time there will be a moderate temperature of about ten degrees of frost, while due to temperature differences periodic thaws can be observed. Severe cooling down to -30 o C is possible several times during the season. Approximately the same thing will happen in spring and summer - most of the time there will be quite wet and cool weather characteristic of a cyclone, and periodically it will be disturbed by energy surges leading to the establishment of an anticyclone .
In general, nature will try to cover its surface with clouds, so the weather characteristic of the cyclone will be the most common. At the same time, atmospheric phenomena will be characterized by considerable instability, and precipitation in the form of wet snow or rain may begin several times a day and suddenly cease, after which the sky can suddenly clear up allowing the sun’s rays to nourish the earth with their energy. Such cycles will be accompanied by active winds, which will rapidly transfer air masses with different humidity, temperature and density, thereby varying the weather conditions at each point on Earth. It should be borne in mind that some gusts of wind may be particularly strong and develop into hurricanes, and such an undesirable natural phenomenon may become the main form of cataclysm characteristic of central Russia. Similar phenomena have already begun to occur in recent years, and in 2018 they are able to intensify.
In addition, due to frequent precipitation in some places flooding can occur, and such phenomena can be expected next spring. Most likely, in the coming year, fluctuations in the natural environment will not be so severe, which means floods and hurricanes will not cause serious damage. In addition, the security services of your country are well prepared for such incidents, so you can not be afraid of serious consequences. Nevertheless, it is worthwhile to be attentive at those moments when the wind suddenly increases, which may indicate the arrival of another atmospheric front and an abrupt change in the weather. Forecasters are not always able to predict such differences, and therefore the security services are not always able to notify people in advance of a possible hurricane. Of course, we are talking about the most obvious activation of the atmosphere and wind gusts above 15 m / s. In other cases, strong wind will become quite commonplace, which is the main tool of the natural system for varying its parameters.
Weather fluctuations can affect not only the physiology of animals and plants, but also lead to the restructuring of the human body. In general, a sharp change in external conditions makes any creature rebuild, and man as part of the natural environment will feel new energy rhythms manifested in the fluctuations in temperature, humidity and pressure. Such contrasts will be some stress for the body, which will help manifest its hidden resources.
At first, a person may feel overexcitement associated with an increase in the level of vital energy, but later he will have the opportunity to direct this excess force on his undertakings and on the activation of many abilities. The year 2018 can be considered a turning point in many social processes, since the events of 2017 were the result of a general glow of the situation, and now this tension should result in some kind of change. At first glance, stress can create nothing but destruction, and perhaps some social processes will actually experience scrapping. But most likely, these events will not lead to serious consequences, and the social system will easily balance the balance. In general, the social system will act like the natural environment, creating many private bursts and disturbances.
This nature of social phenomena, which will manifest itself in their deviations from the norm, is associated with the reaction of the social system to the cosmic radiation stream, which began to come to Earth from 2017. The set of these frequencies is completely uncharacteristic for the Earth; therefore, new vibrations derive natural and social processes from the usual channel. At the same time, the flow of new energies is constantly changing, and completely different oscillations can be observed, when each pulse is distinguished by its own set of frequencies and a certain intensity of the processes it stimulates.
In most cases, the natural and social systems will not be able to predict the range of frequencies on which influence from space will take place, and they will simply have to react to the changes that will be triggered as part of their phenomena. The same can be said about the human body, whose biological systems will adapt to the new frequencies, and it is impossible to foresee the nature of the external influence. On the one hand, such an effect of surprise can lead to internal excitement, a feeling of insecurity, and for some time the human body will not understand what is happening to it. On the other hand, such destabilization will lead to the need of the body to use its energy reserves, and due to this the level of vital energy will increase. Perhaps, if a person is ready for unexpected mood swings associated with the inability of the body to predict environmental conditions, he can easily go through the process of his activation.
In fact, the human body will experience an awakening and will be able to abandon many of the reflexes and instincts that are annoying to it, which at first will begin to remind of themselves due to an abrupt change of conditions. First of all, natural phenomena will have an impact on humans, the drops of which will begin to be felt by the body and lead to internal agitation. Such a state is associated with the survival instinct, directing the creature’s attention to any uncharacteristic change in the external environment for making a vital decision. In most cases, deviations of natural phenomena from the norm will not lead to cataclysms, but the self-preservation instinct will constantly signal danger. This biological program can be so intensified that it will be uncomfortable for a person to exist with her, and he will be able to cancel it if he is aware of its inefficiency.
Until now, the instinct of self-preservation manifested itself on an unconscious level, forcing a person to compete with other people for social resources. But now, due to especially obvious and frequent fluctuations of the external environment, this instinct will become too obvious, and will lead to inappropriate behavior. A person will feel that in many situations his reactions will turn out to be inappropriate and too hypertrophied, and the reason will be an overabundance of emotions. In order not to let your consciousness loosen up, you should look at yourself from the outside and see that most of the situations that lead to excitement are quite ordinary. Continuing to observe his behavior, a person will be able to feel an internal program that constantly makes him annoyed at every occasion, and the reason will be in the new and unusual vibrations, at which every phenomenon will begin to resonate, at the subconscious level influencing the person’s perception.
The habitual reaction to new energies is a shock and surprise, since the body does not have a ready-made pattern of behavior in unusual energy conditions. At the same time, outwardly, everything can remain the same, and at the level of feelings, the human body will exist at completely new frequencies. In fact, a change in the energy situation is favorable, since it contributes to the restructuring of the structure of the human body and the manifestation of its individuality in the characteristics of its body. Each person can conduct a process similar to that which will occur in nature due to the arrival of new energies. The excess of vital energy caused by the activation can be directed to the awakening of the desired abilities, and then the external influence will no longer lead to irritation. However, it should be borne in mind that before a person needs to remove the lock from his body, canceling the survival program.
One way or another, the external environment contributes to such a step, and by constantly fluctuating its conditions, it stimulates the abandonment of old programs. Such impulses make it possible to realize a survival program, the control of which in most situations turns out to be inappropriate. By drawing attention to this outdated instinct, you can simply stop noticing it, and then the person will release energy from the program that previously controlled his actions. A person will no longer want to respond to these alarming signals arising inside him, and deprived of energy, they will gradually begin to calm down. Due to this, a person will become more a master of his emotions, will be able to direct their power to awakening new abilities and to the realization of their desires, for the realization of which he previously lacked vital resources. Therefore, as the cause of unrest and awareness of habitual reactions is realized, a person will begin to free his perception from old stereotypes, which will help him to find contact with many deep-seated aspirations that were previously unable to materialize due to the lack of sufficient energy.
Thus, in 2018, a person will feel the numerous fluctuations of the external environment, which will lead to a rise in the level of his vital energy. Internal activation will be associated with the body's need to adapt to new conditions, because it will not have ready-made templates for such changes. However, in most cases a person does not need to take any action, and such subconscious reactions are associated with the work of a survival program. Having seen the inexpediency of the majority of emotional surges caused by the work of the survival instinct, a person will be able to center his attention and direct vital resources to his own activation.
In 2018, there will not be a fundamental restructuring at the level of the body, however, having become more free at the state level, a person will create the prerequisites for the desired changes. The key value of the coming year lies in the possibility of canceling many innate programs that will become especially noticeable and thus appear inappropriate, with the result that the need to abandon them will become apparent.
Such a refusal can be made by simply shifting attention to the desired accomplishments after the person has seen the nature of the influence of the internal program on his actions. If the program leads to frequent irritation at the close, then it can be canceled by creating an intention to improve these relations. If irritation is manifested in some activity, then a favorable decision leading to the abolition of the stereotype may be associated with the setting of a goal conducive to self-development. In general, the translation of attention is associated with the creation of a new positive program that replaces the old and effectively implements the amount of energy that was previously spent on unreasonable excitement. The coming year will in many respects allow a person to become the master of his life force and by creating new intentions to direct it to the direction desired for himself.
Respectfully,
It seems that every year the weather is becoming more crazy than the previous one. In the news, in fact, all the time talking about stormy floods and other extreme weather conditions - some may argue with this, but it seems that climate change caused by human activity is actually quite real. Polar icebergs are melting at an alarming rate, which will inevitably cause sea level rise in the future. On the other hand, the period of high fire danger in the forests of hot, arid regions of the west coast of North America lasts about 75 days longer than it lasted ten years ago. Yes, climate change seems inevitable, however, there are still some rather rare natural meteorological phenomena that are to be feared.
1. Rain from animals: drizzle with people, that is, animals, hallelujah
Stories about rains from animals or objects appeared in the first century of our era, when Pliny The Elder first documented frogs falling from the sky. In 1794, French soldiers also witnessed rain from toads. Even today, the people of Honduras have witnessed a phenomenon known as the Fish Rain in Honduras (Lluvia de Peces).
What is Fish Rain in Honduras, you ask? In the department of Yoro, Honduras, literally a fish falls from the sky, and this happens annually for more than a century.
One common explanation for rain from animals falling from the sky is tornadoes, but the closest sea source for the Fish Rain phenomenon in Honduras is more than 200 kilometers away, and tornadoes just do not travel that far. This event may also be due to the fact that freshwater fish travels through groundwater due to seasonal changes. Torrential rains may wash the fish up and, when the water recedes, the fish ends up on the ground.
Some believe that when the Spanish priest José Manuel (Jesus de) Subirana (Father José Manuel (Jesus de) Subirana) saw how poor and hungry the local people of Yoro were, he prayed that this wonderful gift of food would be given to this people. After praying for three days and three nights, people were gifted with this rain of fish.
This rain of fish unwittingly makes one wonder if the Shark Tornado can become a reality?
2. Leaky cloud: UFO or not?
Some people see really weird things and others see what they want to see. Take, for example, the recent history of people in Stockton, California, who claimed to have seen a huge hole in the sky. These viewers went to social media and began to express their assumptions that the hole was caused by anything, from an alien spacecraft to an intergalactic wormhole. In fact, the UFO was a leaky cloud, also known as a perforated cloud.
Cirro-cumulus or Altocumulus clouds containing super-cooled water that cannot freeze without a tiny particle to catch on are the main cause of the formation of leaky clouds. Scientists believe that when planes fly through these clouds, they begin the process of ice formation and crystallization. The air passing around the propellers or wings of the aircraft causes the air to expand and cool quickly, thus forming ice crystals, which then descend below the cloud, long after the aircraft has passed through it. Perhaps one of these leaky clouds inspired the classic Black Sabbath song called “Hole In The Sky” (Hole In The Sky):
"I look through the hole in the sky
I can't see anything through the eyes of a lie
I am nearing the end of the line
I live with ease when the sun does not shine "
3. Fiery Whirlwind: When Forest Fires Turn into Tornado Whirling
The fire vortex is a rare phenomenon in which fire forms a tornado-like vortex of flame. These insidious cyclones of the flame are also known as fire-smoke whirlwinds or fire devils, and no wonder - they look as if they came directly from the deepest depths of hell!
These hellish whirling dervishes of fire arise when the trees, the hillside, or the flames cause the air to shift against competing air temperatures and speeds. Although some fire vortices fade out rather quickly, others can move when the heat is able to stay at a certain level and the surrounding gases push it away to itself.
Perhaps the deadliest example of a whirlwind of fire happened in 1923 in Japan, becoming the consequence of a powerful earthquake of 7.9 points. The survivors of the catastrophe gathered in an open space, but the resulting massive fiery whirlwind passed through the entire region, killing thousands.
4. Lightning Catatumbo: the largest and longest light show on earth
You have heard the term "perfect storm", haven't you? Yes, an ideal storm, where a series of events occurs simultaneously, which greatly aggravates the situation. This lightning phenomenon is so rare that it only happens in one place on Earth because of the ideal location storm and natural gases.
The lightning phenomenon Catatumbo is found only over the mouth of the Catatumbo River in Venezuela, where it flows into Lake Maracaibo. Warm and cold fronts collide, creating the ideal condition for this lightning. Add to this the nearby swamps that emit methane, which in turn improves the electrical conductivity of the clouds - and voila! You got the coolest atmospheric phenomenon.
Catatumbo lightning bolts usually occur for 140–160 nights a year, but ceased to appear within a few months in 2010, which caused many locals to worry. Much to their relief, the lightning has since returned, and now they are stronger than ever.
5. A rounded-horizontal arc or “fiery rainbow”: an air kaleidoscope of color
Fire rainbows look so cool and happen so rarely that, quite possibly, the Land of Oz is really somewhere above them!
Technically known as circular-horizontal arcs, these rainbows occur under very specific conditions. They usually appear during the summer months - the sun should be at an altitude of 58 ° or more, with cirrus clouds and sunlight passing through ice crystals in the clouds at the right angle.
It is also one of the biggest clouds! They are so large that some mistakenly take the rainbow for a part of the sky, not a cloud.
Round-horizontal arcs, also known as the ice halo, are in fact neither fire nor rainbow.
6. Ice stalactite (Вrinicle): icy finger of death
Dangerous weather events pose a threat not only to us, the inhabitants of the land, they also threaten some of our sea friends.
Take, for example, cool and bizarre-looking ice stalactite. Ice stalactite is formed by lowering to the bottom of a cold, saline solution (water, saturated with salt).
It is formed when the heat rises from the warm sea to the cold air, as a result of which new ice forms at the bottom. Ice is pushed through the channels of salt water and because this salt water is denser and colder than the rest of the sea water surrounding it, it sinks down and freezes areas of warmer sea water with which it comes in contact. When ice stalactite reaches the bottom, it leaves a deadly web of ice that freezes everything it comes into contact with, including sea urchins and starfish.
Be careful, Aquaman!
7. Green ray: blink and miss it!
If you've ever seen a piece of green peeking out from behind the sun at sunrise or sunset, this could be one of two things:
1) Either you have a memory from an acid trip
or
2) Either you have witnessed a natural phenomenon known as the green ray.
This phenomenon usually occurs during sunrise or sunset, when more light reaches the eye of the observer without scattering. The green beam is due to the slight bending and refraction of light in the atmosphere. The atmosphere acts as a prism, dividing the light into different colors. When the sun rises completely above the horizon, the different colors of the spectrum merge, making the spectrum invisible to the naked eye. It is called a ray, because it is precisely this that it is - the green color is visible only for a few seconds.
However, if you took an acid, before observing this phenomenon, you will be able to see a lot more than a green spot above the sun!
8. Dirty thunderstorm: a storm in a volcano
Let's talk a little more about lightning, just because they are damn cool!
Another truly fascinating and rare weather phenomenon is volcanic lightning, also known as the dirty thunderstorm. In this phenomenon, there is not only a formidable look and danger of a volcanic eruption, lightning is also mixed in here, and as a result you get a blood-curdling miracle of weather!
Volcanic lightning happens when lightning forms in a volcanic column of smoke and ash. The process begins when the particles are separated, either after a collision, or when large particles are split in two. Then some differences in the aerodynamics of these particles cause the positively charged particles to separate from the negatively charged particles. Lightning happens when this charge separation becomes too large and the air cannot withstand the flow of electricity. Volcanic eruptions also release large amounts of water, which can also contribute to the formation of these thunderstorms.
Advice for the future: if you see a lightning in the very center of a volcanic eruption, take out the legs of urine from there!
9. Aurora: Nature's impressive light show
We just had to include the aurora in this list! This is an incredible natural phenomenon that occurs above the magnetic poles in the north and is also known as the northern lights. (In the south, the same thing happens, but it is known as the southern lights).
What causes the formation of these auroras? And again, the whole thing is a collision. This incredible light show occurs when the gaseous particles of the earth’s atmosphere collide with charged particles coming from the sun that enter the earth’s atmosphere. These fantastic displays, which are usually seen closer to the poles and during the days of the equinox, appear in many colors, although green and pink are the most common.
Representatives of the Indian people Menominee from Wisconsin believed that the northern lights are the seat of the spirits of the great hunters.
10. Gross Clouds: Waves that roll across the sky.
Gross clouds are a truly spectacular sight! Some people described these clouds as overturned tornadoes. These types of gross clouds are usually associated with thunderstorms.
Do not confuse them with similar shelf clouds. These rarities of nature are formed when the air temperature is inverted, which is why warm air is above the cold air. Then the wind changes its speed and direction, and forces these clouds to roll up.
For the formation of gross clouds need only the right amount of moisture. Storm winds actually roll the clouds into a tubular shape that moves ahead of the storm. They look like a giant rolling pin rolling across the sky!